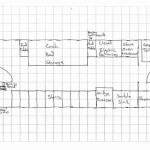
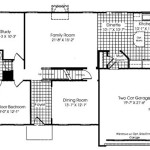
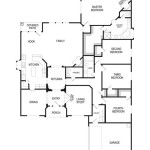
A 2D floor plan is a scaled drawing that depicts the layout of a building’s floor plan from above. It shows the arrangement of rooms, walls, doors, and windows, providing a visual representation of the space. Floor plans are commonly used in architecture, interior design, and real estate.
2D floor plans are essential for planning and designing buildings. They allow architects and interior designers to visualize and optimize the use of space, ensuring that the layout is functional and meets the specific requirements of the project. Floor plans are also used in the construction phase to guide the placement of walls, fixtures, and other building components.
Transition Paragraph:
Understanding the elements and key features of a 2D floor plan is crucial for effectively interpreting and utilizing it. Let’s explore the different components that make up a floor plan and how they contribute to its overall functionality.
2D floor plans are characterized by several important points that contribute to their effectiveness:
- Scale
- Symbols
- Dimensions
- Layout
- Walls and Openings
- Furniture
- Materials
- Annotations
These elements work together to create a comprehensive representation of the building’s floor plan, facilitating informed decision-making and effective communication among architects, designers, contractors, and clients.
Scale
Scale is a crucial aspect of 2D floor plans as it determines the accuracy and usefulness of the drawing. It refers to the ratio between the size of the drawing and the actual size of the building or space it represents.
Floor plans are typically drawn to scale, which means that a specific unit of measurement on the plan corresponds to a specific unit of measurement in the real world. This allows architects, designers, and other professionals to accurately plan and design buildings, ensuring that the dimensions and proportions of the spaces are correct.
Scales are usually expressed as a ratio, such as 1:50 or 1:100. A scale of 1:50 means that one unit on the plan represents 50 units in the actual building. For example, if a wall is drawn as 10 centimeters long on the plan, it would be 500 centimeters (5 meters) long in reality.
Choosing the appropriate scale for a floor plan depends on the size and complexity of the building or space being represented. Smaller buildings or spaces may require a larger scale (e.g., 1:20 or 1:25) to show more detail, while larger buildings or spaces may require a smaller scale (e.g., 1:100 or 1:200) to fit the entire plan on a single sheet.
Maintaining accurate scale is essential for ensuring that the floor plan is a reliable representation of the actual space. It allows architects, designers, and contractors to make informed decisions based on the plan, ensuring that the building is constructed according to the intended design.
Symbols
Symbols are an essential element of 2D floor plans, as they represent various objects and elements of the building or space in a standardized and universally understood manner.
- Walls
Walls are typically represented by thick lines, with different line weights indicating different wall types (e.g., exterior walls, interior walls, load-bearing walls, etc.).
- Doors
Doors are represented by small rectangles or arcs, with the direction of the door swing indicated by a short line or arrow.
- Windows
Windows are represented by rectangles or squares, with the type of window (e.g., casement window, double-hung window, etc.) often indicated by specific symbols or shading.
- Stairs
Stairs are represented by a series of parallel lines, with the direction of the stairs indicated by arrows or small triangles.
These are just a few examples of the many symbols used in 2D floor plans. By understanding these symbols, architects, designers, and other professionals can quickly and easily interpret floor plans, facilitating effective communication and decision-making throughout the design and construction process.
Dimensions
Dimensions are a critical aspect of 2D floor plans, as they provide precise measurements of the building or space, ensuring that the design is accurate and functional.
- Overall Dimensions
Overall dimensions refer to the total length and width of the building or space, as measured from the exterior walls. These dimensions determine the overall footprint of the building and help architects and designers plan the layout of the interior spaces.
- Room Dimensions
Room dimensions specify the length and width of each individual room within the building or space. These dimensions are crucial for determining the size and functionality of each room, ensuring that there is sufficient space for furniture, equipment, and other elements.
- Wall Lengths
Wall lengths indicate the length of each wall within the building or space. These dimensions are important for calculating the amount of materials needed for construction, such as drywall, paint, and flooring.
- Door and Window Dimensions
Door and window dimensions specify the height and width of each door and window opening. These dimensions are essential for selecting the appropriate doors and windows and ensuring that they fit properly within the openings.
Accurate dimensions are essential for ensuring that the floor plan is a reliable representation of the actual space. They allow architects, designers, and contractors to make informed decisions based on the plan, ensuring that the building is constructed according to the intended design.
Layout
Layout refers to the arrangement of rooms, spaces, and elements within a building or space, as depicted in a 2D floor plan. It encompasses the overall organization and flow of the space, ensuring that it is functional, efficient, and aesthetically pleasing.
Effective layout planning considers various factors, including the intended use of the space, the number of occupants, and the desired level of privacy and accessibility. Architects and designers carefully consider the relationships between different spaces, ensuring that they are connected logically and that the transitions between them are smooth and seamless.
The layout of a building or space can have a significant impact on its overall functionality and livability. A well-planned layout can maximize natural light, improve ventilation, and create a sense of spaciousness, while a poorly planned layout can lead to cramped, inefficient, and uncomfortable spaces.
Layout planning also involves considering the placement of furniture, equipment, and other elements within each space. By carefully arranging these elements, architects and designers can create spaces that are both functional and visually appealing, ensuring that the occupants can move around comfortably and perform their activities effectively.
Walls and Openings
Walls and openings are essential components of 2D floor plans, defining the boundaries of spaces and facilitating movement and access within a building or space.
- Walls
Walls are vertical structures that divide and enclose spaces within a building or space. They provide structural support, privacy, and protection from the elements. Walls can be load-bearing, meaning they support the weight of the building above, or non-load-bearing, meaning they are supported by other structural elements such as beams or columns.
- Doors
Doors are openings in walls that allow for movement between spaces. They can be hinged, sliding, or revolving, and come in various sizes and styles to suit different functional and aesthetic requirements.
- Windows
Windows are openings in walls that allow for natural light and ventilation. They can be fixed, operable, or a combination of both, and come in various shapes and sizes to suit different architectural styles and functional needs.
- Other Openings
Other types of openings in walls can include arches, skylights, and vents. Arches are curved openings that can add architectural interest and grandeur to a space. Skylights are openings in the roof that allow for natural light to enter a space. Vents are small openings that allow for air circulation and ventilation.
The placement and design of walls and openings have a significant impact on the overall functionality, aesthetics, and energy efficiency of a building or space. Careful consideration must be given to the size, shape, and location of these elements to ensure that they meet the specific requirements of the project.
Furniture
Furniture plays a crucial role in 2D floor plans as it defines the functionality and aesthetics of each space within a building or structure. Architects and designers carefully consider the placement and selection of furniture to create spaces that are both visually appealing and functional.
The type and arrangement of furniture can influence the flow of movement within a space, create focal points, and define different zones or areas for specific activities. For instance, in a living room, a sofa and armchair might be arranged around a coffee table to create a cozy seating area, while in a dining room, chairs and a table are positioned to facilitate comfortable dining.
2D floor plans often use symbols or representations to indicate the size and shape of furniture. These symbols can vary depending on the scale and level of detail required in the plan. For example, a bed might be represented by a rectangle, while a sofa might be shown as a curved shape.
The inclusion of furniture in 2D floor plans allows architects and designers to visualize how a space will be furnished and used, ensuring that the layout is functional and meets the specific requirements of the project. It also provides valuable information for contractors during the construction phase, helping them to accurately install electrical outlets, lighting, and other fixtures in relation to the furniture layout.
In addition to its functional importance, furniture can also contribute to the overall aesthetic and ambiance of a space. By carefully selecting furniture pieces that complement the architectural style and color scheme, designers can create harmonious and inviting environments.
Materials
Materials play a crucial role in the construction and design of buildings and spaces, and their specification is an essential aspect of 2D floor plans. Architects and designers carefully select materials based on their functional properties, aesthetic qualities, and cost considerations.
The choice of materials can significantly impact the durability, energy efficiency, and overall performance of a building or space. For instance, the use of sustainable materials can reduce environmental impact and contribute to a healthier indoor environment. Similarly, the selection of materials with specific acoustic properties can help control noise levels and improve the overall comfort of occupants.
In 2D floor plans, materials are typically indicated using abbreviations or symbols to represent different types of materials used in the construction of walls, floors, and other building elements. For example, “CMU” may be used to represent concrete masonry units, while “GWB” may indicate gypsum wallboard.
The specification of materials in 2D floor plans is essential for contractors and builders to accurately estimate the cost of construction and ensure that the building meets the required building codes and standards. It also provides valuable information for maintenance and renovation purposes, allowing facility managers to identify and source the appropriate materials for repairs or upgrades.
In addition to their functional importance, materials can also contribute to the aesthetic and ambiance of a space. By carefully selecting materials that complement the architectural style and color scheme, designers can create harmonious and inviting environments.
Annotations
Annotations are essential elements of 2D floor plans, providing additional information and instructions that help clarify the design intent and facilitate efficient construction. These annotations can range from simple notes to detailed specifications, and they play a crucial role in ensuring that the building or space is constructed according to the architect’s or designer’s vision.
- Dimensions and Measurements
Dimensions and measurements are critical annotations that provide precise information about the size and scale of various elements within the floor plan. These annotations include the overall dimensions of the building or space, as well as the dimensions of individual rooms, walls, doors, and windows. Accurate dimensions are essential for ensuring that the building is constructed to the correct specifications and that all elements fit together properly.
- Materials and Finishes
Annotations related to materials and finishes specify the types of materials to be used in the construction of walls, floors, ceilings, and other building components. These annotations may also include information about the color, texture, and pattern of the materials, ensuring that the finished space matches the design intent. Clear specifications of materials and finishes help contractors and builders to accurately estimate costs and ensure that the building meets the desired aesthetic and functional requirements.
- Equipment and Fixtures
Annotations for equipment and fixtures indicate the location and type of equipment and fixtures to be installed within the building or space. These annotations may include symbols or abbreviations to represent specific fixtures, such as sinks, toilets, appliances, and lighting fixtures. Accurate placement of equipment and fixtures is crucial for ensuring that the space is functional and meets the specific needs of the occupants.
- Construction Details
Construction details are annotations that provide specific instructions or details about how certain elements of the building or space should be constructed. These annotations may include information about the type of construction methods to be used, the sequence of construction, and any special requirements or considerations. Construction details help to ensure that the building is constructed safely and efficiently, and that it meets the required building codes and standards.
Annotations in 2D floor plans are essential for effective communication between architects, designers, contractors, and builders. By providing clear and detailed information, annotations help to reduce errors, ensure accurate construction, and facilitate efficient project execution.









Related Posts