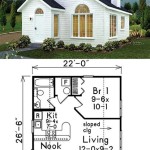
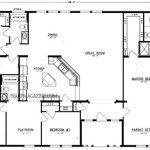
Container homes floor plans are detailed blueprints that outline the layout and design of a house constructed from shipping containers. These plans encompass the arrangement of rooms, placement of windows and doors, and specification of fixtures and materials. For instance, a two-bedroom container home floor plan might incorporate a living room, kitchen, bathroom, and two bedrooms within the confines of two 20-foot shipping containers.
Floor plans for container homes are essential for ensuring efficient use of space, maximizing natural light, and creating a comfortable and functional living environment. They serve as a roadmap for the construction process, providing guidance on the placement of walls, partitions, and electrical and plumbing systems.
In the following sections, we will explore the key components of container homes floor plans, discuss the advantages of using containers as building blocks, and provide examples of innovative and sustainable floor plan designs.
When designing container homes floor plans, there are several important points to consider:
- Container Size and Dimensions: Standard shipping containers come in various sizes, so choose the ones that best fit your space requirements.
- Layout and Flow: Plan the arrangement of rooms and spaces to maximize natural light and create a functional flow.
- Insulation and Ventilation: Ensure proper insulation and ventilation to maintain a comfortable indoor environment.
- Utilities and Systems: Determine the placement of electrical, plumbing, and HVAC systems to support the home’s needs.
- Exterior Finishes: Consider exterior finishes that complement the container’s industrial aesthetic or enhance its curb appeal.
- Sustainability: Opt for eco-friendly materials and design features to reduce the environmental impact.
- Customization: Tailor the floor plan to your specific needs and preferences, including the addition of windows, doors, or mezzanines.
- Building Codes: Comply with local building codes and regulations to ensure safety and structural integrity.
Following these points will help you create well-designed and functional container homes floor plans.
Container Size and Dimensions: Standard shipping containers come in various sizes, so choose the ones that best fit your space requirements.
When selecting shipping containers for your container home, it’s crucial to consider their size and dimensions to ensure they meet your space requirements and design vision. Standard shipping containers come in a range of sizes, with the most common being 20 feet and 40 feet in length. Other less common sizes include 10 feet and 45 feet containers.
- 20-foot containers: Measuring 20 feet in length, 8 feet in width, and 8 feet 6 inches in height, these containers are ideal for smaller homes, studios, or guest houses. They offer a compact and efficient use of space, making them suitable for urban areas or tight building sites.
- 40-foot containers: With dimensions of 40 feet in length, 8 feet in width, and 8 feet 6 inches in height, 40-foot containers provide more space and flexibility for larger homes or commercial buildings. They can accommodate multiple rooms, including bedrooms, bathrooms, kitchens, and living areas.
- 10-foot containers: Less commonly used for residential purposes, 10-foot containers measure 10 feet in length, 8 feet in width, and 8 feet 6 inches in height. They are suitable for small storage units, workshops, or as additions to larger container homes.
- 45-foot containers: Measuring 45 feet in length, 8 feet in width, and 9 feet 6 inches in height, 45-foot containers offer even more space than 40-foot containers. They are ideal for spacious homes, commercial buildings, or industrial applications.
Choosing the right container size is essential for optimizing space utilization, minimizing wasted space, and ensuring a comfortable and functional living environment in your container home.
Layout and Flow: Plan the arrangement of rooms and spaces to maximize natural light and create a functional flow.
When planning the layout and flow of your container home, consider the following points to maximize natural light and create a functional living space:
- Maximize Windows and Skylights: Position windows and skylights strategically to allow ample natural light to enter the home. Place windows on multiple walls to create cross-ventilation and reduce reliance on artificial lighting.
- Open Floor Plan: Consider an open floor plan to enhance the flow of light and air throughout the home. This layout eliminates unnecessary walls and partitions, creating a more spacious and inviting atmosphere.
- Multi-Level Design: If your container home has multiple levels, design the layout to allow natural light to penetrate both levels. Use large windows and skylights on the upper level to bring in light, while incorporating clerestory windows or light tubes to direct light to the lower level.
- Room Placement: Plan the placement of rooms to take advantage of natural light. Position living areas and bedrooms where they will receive the most sunlight, while placing utility spaces like bathrooms and storage areas in less sunlit areas.
By carefully considering the layout and flow of your container home, you can create a bright, airy, and comfortable living environment that maximizes the benefits of natural light.
Insulation and Ventilation: Ensure proper insulation and ventilation to maintain a comfortable indoor environment.
Insulation
Insulating your container home is crucial for maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature and reducing energy consumption. Proper insulation prevents heat loss in cold climates and keeps the home cool in warm climates. Choose insulation materials that are specifically designed for shipping containers, as they are typically thinner and more flexible than traditional insulation materials. Common insulation options for container homes include:
- Spray foam insulation: This insulation is applied as a liquid that expands and hardens to fill all gaps and cavities, creating a seamless and airtight seal. It provides excellent insulation values and can also act as a vapor barrier.
- Rigid foam insulation: Available in sheets or boards, rigid foam insulation is easy to install and provides good thermal resistance. It is less effective as a vapor barrier compared to spray foam insulation.
- Batt insulation: Batt insulation is made of fiberglass or cellulose and is installed between the studs or joists of the container walls and roof. It is a cost-effective option but requires more labor to install and may not provide as good insulation as spray foam or rigid foam.
Ventilation
Proper ventilation is essential for maintaining a healthy and comfortable indoor environment in your container home. Ventilation systems allow fresh air to circulate, remove excess moisture, and prevent the buildup of pollutants. There are two main types of ventilation systems used in container homes:
- Natural ventilation: This relies on natural airflow through windows, doors, and vents to circulate air. It is a low-cost and energy-efficient option, but it may not be sufficient in all climates or during extreme weather conditions.
- Mechanical ventilation: This uses fans or other mechanical devices to circulate air throughout the home. It provides more control over ventilation and can be used to improve air quality and remove pollutants.
When designing your container home floor plan, consider the placement of windows, doors, and vents to maximize natural ventilation. Additionally, plan for the installation of a mechanical ventilation system to ensure adequate air circulation and indoor air quality.
Utilities and Systems: Determine the placement of electrical, plumbing, and HVAC systems to support the home’s needs.
Electrical System
The electrical system in a container home is responsible for providing power to all electrical appliances and devices. It includes wiring, outlets, switches, and a main electrical panel. When planning the electrical system for your container home, consider the following:
- Power Requirements: Determine the total power requirements for your home, including the appliances, lighting, and other electrical devices you will be using. This will help you determine the size of the electrical panel and wiring needed.
- Circuit Layout: Plan the layout of the electrical circuits to ensure that each circuit has a dedicated purpose and is not overloaded. Separate circuits should be used for lighting, outlets, and high-power appliances.
- Conduit and Wiring: Choose the appropriate conduit and wiring materials for your container home. Conduit protects the electrical wires from damage and moisture, while the wiring should be rated for the specific electrical load it will carry.
- Outlet and Switch Placement: Plan the placement of outlets and switches for maximum convenience and functionality. Consider the location of furniture and appliances when determining the optimal placement of outlets and switches.
Plumbing System
The plumbing system in a container home is responsible for supplying water and draining waste. It includes pipes, fixtures, and appliances such as sinks, toilets, and showers. When planning the plumbing system for your container home, consider the following:
- Water Source: Determine the source of water for your home, whether it is a municipal water supply, well, or rainwater harvesting system.
- Pipe Sizing and Layout: Choose the appropriate pipe sizes and layout to ensure adequate water pressure and flow throughout the home. Plan the layout to minimize the risk of leaks and freezing.
- Fixture Placement: Plan the placement of plumbing fixtures, such as sinks, toilets, and showers, to ensure functionality and convenience. Consider the location of windows and doors when determining fixture placement.
- Drainage System: Design the drainage system to effectively remove wastewater from the home. This includes installing drains, traps, and a septic tank or other wastewater treatment system.
HVAC System
The HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) system in a container home is responsible for maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature and air quality. It includes heating and cooling units, ductwork, and air filters. When planning the HVAC system for your container home, consider the following:
- Climate Zone: The climate zone in which your home is located will determine the type of HVAC system required. Consider the average temperatures and humidity levels in your area.
- Heating and Cooling Needs: Determine the heating and cooling needs for your home based on its size, insulation, and orientation. This will help you select the appropriate size and type of HVAC unit.
- Ductwork Layout: Plan the layout of the ductwork to ensure efficient distribution of heated or cooled air throughout the home. Consider the location of rooms, windows, and doors when determining ductwork placement.
- Air Filtration: Choose an HVAC system with an effective air filtration system to remove allergens, dust, and other pollutants from the air.
Exterior Finishes: Consider exterior finishes that complement the container’s industrial aesthetic or enhance its curb appeal.
Corrugated Metal
Corrugated metal is a popular choice for container homes due to its durability, low cost, and industrial aesthetic. It is available in a variety of colors and finishes, allowing you to customize the look of your home while maintaining its industrial roots. Corrugated metal is also easy to install and maintain, making it a practical option for DIY builders.
Wood
Wood is another popular choice for container homes, as it offers a more traditional and natural look. Wood siding can be painted or stained to match your desired aesthetic, and it can be used to create a variety of different looks, from rustic to modern. Wood is also a relatively sustainable material, making it a good choice for eco-conscious builders.
Stucco
Stucco is a durable and low-maintenance exterior finish that can give your container home a more traditional look. It is available in a variety of colors and textures, allowing you to customize the look of your home to match your taste. Stucco is also fire-resistant and can help to insulate your home, making it a good choice for both form and function.
Composite Cladding
Composite cladding is a low-maintenance and durable exterior finish that is made from a combination of wood and plastic. It is available in a variety of colors and textures, and it can be used to create a variety of different looks. Composite cladding is also resistant to rot, insects, and fire, making it a good choice for homes in harsh climates.
Other Finishes
In addition to the above options, there are a variety of other exterior finishes that can be used on container homes. These include vinyl siding, fiber cement siding, and stone veneer. The best finish for your home will depend on your personal taste, budget, and climate.
Sustainability: Opt for eco-friendly materials and design features to reduce the environmental impact.
Use Recycled and Sustainable Materials
One of the best ways to reduce the environmental impact of your container home is to use recycled and sustainable materials. This includes using recycled shipping containers themselves, as well as other materials such as reclaimed wood, bamboo, and recycled plastic. These materials help to reduce waste and conserve natural resources.
Design for Energy Efficiency
Another important aspect of sustainable container home design is energy efficiency. This can be achieved through a variety of means, such as using energy-efficient appliances, installing solar panels, and designing the home to take advantage of natural light and ventilation. These measures can help to reduce your energy consumption and carbon footprint.
Incorporate Green Features
There are many other green features that you can incorporate into your container home design to reduce its environmental impact. These include:
- Using rainwater harvesting systems to collect and store rainwater for non-potable uses, such as irrigation and flushing toilets.
- Installing low-flow appliances and fixtures to reduce water consumption.
- Using natural and non-toxic building materials to improve indoor air quality.
- Landscaping with native plants to reduce water usage and support local wildlife.
Reduce Waste and Emissions
During the construction and operation of your container home, there are many ways to reduce waste and emissions. These include:
- Recycling and composting construction waste.
- Using low-VOC (volatile organic compound) paints and finishes.
- Driving less by walking, biking, or using public transportation.
- Choosing renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power.
By incorporating sustainable materials, design features, and practices into your container home, you can reduce its environmental impact and create a more eco-friendly living space.
In addition to the environmental benefits, sustainable container homes can also be more comfortable and healthy to live in. They have better indoor air quality, are more energy-efficient, and can help to reduce your utility bills.
Customization: Tailor the floor plan to your specific needs and preferences, including the addition of windows, doors, or mezzanines.
The beauty of container homes lies in their versatility and adaptability. You can customize your container home floor plan to suit your specific needs and preferences, ensuring that your home is not only functional but also a reflection of your unique style.
- Windows and Doors:
The number, size, and placement of windows and doors in your container home floor plan will impact the amount of natural light, ventilation, and views you have. Consider your desired level of privacy, energy efficiency, and aesthetic preferences when making these decisions.
- Mezzanines:
Adding a mezzanine to your container home floor plan can create additional living space without increasing the overall footprint of your home. Mezzanines are often used to create loft bedrooms, home offices, or storage areas.
- Interior Walls:
While shipping containers provide a sturdy structure, you are not limited to their original layout. You can add or remove interior walls to create rooms of different sizes and configurations, allowing you to tailor the floor plan to your specific needs.
- Exterior Modifications:
In addition to interior modifications, you can also make exterior modifications to your container home, such as adding decks, porches, or awnings. These additions can extend your living space, enhance the aesthetic appeal of your home, and provide additional outdoor enjoyment.
By customizing your container home floor plan, you can create a living space that is not only functional and efficient but also a reflection of your unique style and personality.
Building Codes: Comply with local building codes and regulations to ensure safety and structural integrity.
Building codes are essential regulations that ensure the safety and structural integrity of buildings. When designing and constructing container homes, it is crucial to comply with all applicable building codes and regulations in your local area. These codes address various aspects of construction, including structural design, fire safety, electrical systems, plumbing, and accessibility, among others.
- Structural Design:
Building codes specify minimum requirements for the structural design of buildings to withstand various loads, such as dead loads (weight of the structure), live loads (occupants and furniture), wind loads, and seismic loads (in earthquake-prone areas). Container homes must meet these requirements to ensure the stability and safety of the structure.
- Fire Safety:
Building codes include provisions for fire safety, such as fire-resistant materials, fire separations, and means of egress. Container homes must comply with these requirements to minimize the risk of fire and ensure the safety of occupants in the event of a fire.
- Electrical Systems:
Electrical codes regulate the design and installation of electrical systems in buildings to ensure safety and prevent electrical hazards. Container homes must adhere to these codes to ensure proper electrical wiring, grounding, and protection against electrical shocks and fires.
- Plumbing:
Plumbing codes govern the installation and maintenance of plumbing systems in buildings, including water supply, drainage, and waste disposal. Container homes must comply with these codes to ensure the proper functioning of plumbing fixtures, prevent leaks, and maintain sanitary conditions.
By complying with local building codes and regulations, you can ensure that your container home is safe, structurally sound, and meets the minimum standards for habitability and functionality. Ignoring building codes can compromise the safety of your home and its occupants, and may also lead to legal issues or difficulties obtaining permits and insurance.










Related Posts