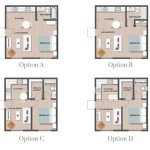
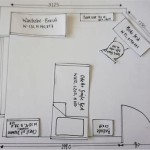
Creating a house floor plan involves laying out the various rooms and spaces within a home, specifying their dimensions, and indicating their relationship to each other. It serves as a blueprint for the home’s construction and determines the flow and functionality of its living spaces. For instance, a well-designed floor plan maximizes natural light, creates seamless transitions between rooms, and optimizes the use of space.
Floor plans are essential during the design and construction phases of a home. They help architects and builders visualize the layout, ensuring that the home meets the specific needs and preferences of the homeowners. They also enable contractors to accurately estimate materials and labor costs, facilitating budget planning and timely project completion.
In this article, we will delve into the key aspects of creating a house floor plan, from initial concept development to the finalization of detailed schematics. We will explore the various considerations, best practices, and software tools used in the process, empowering readers with the knowledge to create functional and aesthetically pleasing floor plans for their dream homes.
Creating a house floor plan involves several important considerations:
- Functionality and flow
- Room size and proportions
- Natural light and ventilation
- Traffic patterns and circulation
- Code compliance and safety
- Energy efficiency and sustainability
- Personal preferences and lifestyle
- Budget and cost-effectiveness
By carefully considering these factors, homeowners and architects can create floor plans that meet their specific needs and aspirations.
Functionality and flow
Functionality and flow refer to the arrangement of rooms and spaces within a house floor plan in a way that optimizes usability, convenience, and accessibility. A well-designed floor plan should allow for smooth transitions between rooms, create logical connections between different areas of the home, and minimize wasted space.
- Adjacency and proximity: Place rooms that are frequently used together or have a natural relationship adjacent to each other. For example, the kitchen should be near the dining room and family room, and bedrooms should be close to bathrooms.
- Traffic flow: Consider the flow of traffic within the home and avoid creating bottlenecks or awkward pathways. Ensure that there are clear and direct routes between common areas, such as the entrance, living room, and kitchen.
- Room size and proportions: The size and proportions of each room should be appropriate for its intended use and the number of people who will be using it. Avoid creating rooms that are too small or cramped, or too large and impersonal.
- Natural light and ventilation: Position windows and doors to maximize natural light and ventilation throughout the home. This can help reduce energy costs and create a more comfortable and healthy living environment.
By carefully considering functionality and flow, homeowners and architects can create floor plans that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also practical and enjoyable to live in.
Room size and proportions
The size and proportions of each room in a house floor plan should be carefully considered to ensure that the space is functional, comfortable, and aesthetically pleasing. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Purpose of the room: The size and proportions of a room should be appropriate for its intended use. For example, a living room should be large enough to accommodate furniture and seating for guests, while a bedroom should be large enough to fit a bed and other necessary furniture.
- Number of occupants: The size of a room should also take into account the number of people who will be using it. A bedroom for a single person can be smaller than a bedroom for a couple or a family.
- Furniture and storage: When determining the size of a room, it is important to consider the furniture and storage that will be needed. Ensure that there is enough space for furniture to be arranged comfortably and that there is adequate storage for belongings.
- Traffic flow: The size and proportions of a room should also allow for easy traffic flow. Avoid creating rooms that are too narrow or cluttered, as this can make it difficult to move around.
By carefully considering the size and proportions of each room, homeowners and architects can create floor plans that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
Natural light and ventilation
Natural light and ventilation are essential for creating a healthy and comfortable living environment. By carefully considering the placement of windows and doors, homeowners and architects can maximize natural light and ventilation throughout the home.
Benefits of natural light and ventilation:
- Improved health: Natural light has been shown to improve mood, boost energy levels, and enhance overall well-being. Ventilation helps to circulate fresh air throughout the home, reducing the risk of respiratory problems and other health issues.
- Reduced energy costs: Natural light can reduce the need for artificial lighting, leading to lower energy costs. Ventilation can also help to regulate indoor temperatures, reducing the need for heating and cooling systems.
- Increased comfort: Natural light and ventilation create a more comfortable and inviting living environment. Homes with plenty of natural light and fresh air are often more enjoyable to live in.
Tips for maximizing natural light and ventilation:
- Orient the home to take advantage of the sun: The orientation of the home can have a significant impact on the amount of natural light it receives. In the Northern Hemisphere, homes that are oriented to the south will receive the most sunlight. In the Southern Hemisphere, homes that are oriented to the north will receive the most sunlight.
- Use large windows and doors: Large windows and doors allow more natural light to enter the home. Consider using floor-to-ceiling windows or sliding glass doors to maximize natural light.
- Place windows and doors strategically: Place windows and doors in areas where they will provide the most natural light and ventilation. For example, place windows in living rooms, bedrooms, and kitchens. Place doors in areas that connect indoor and outdoor spaces.
- Use skylights: Skylights are a great way to bring natural light into dark areas of the home, such as hallways and bathrooms. Skylights can also be used to provide ventilation.
By carefully considering natural light and ventilation, homeowners and architects can create floor plans that are not only functional and aesthetically pleasing but also healthy and comfortable to live in.
Traffic patterns and circulation
Traffic patterns and circulation refer to the flow of people and objects within a house floor plan. A well-designed floor plan should minimize traffic congestion and create a smooth and efficient flow of movement throughout the home.
- Entry and exit points: The entry and exit points of the home should be clearly defined and easily accessible. Avoid creating bottlenecks or awkward pathways at entrances and exits.
- Main circulation routes: The main circulation routes of the home should be wide enough to accommodate multiple people and objects. Avoid creating narrow hallways or doorways that can cause congestion.
- Secondary circulation routes: Secondary circulation routes can be used to provide alternative pathways and reduce traffic on main circulation routes. For example, a secondary circulation route could be used to connect the kitchen to the dining room.
- Connections between spaces: The connections between different spaces in the home should be logical and convenient. For example, the kitchen should be easily accessible from the dining room and family room.
By carefully considering traffic patterns and circulation, homeowners and architects can create floor plans that are not only functional and aesthetically pleasing but also safe and easy to navigate.
Code compliance and safety
Code compliance and safety are essential considerations when creating a house floor plan. Building codes are regulations that govern the design and construction of buildings to ensure the health, safety, and welfare of occupants. Floor plans must comply with all applicable building codes to obtain a building permit and ensure the safety of the home.
Some of the key code compliance and safety considerations for house floor plans include:
- Fire safety: Fire safety codes dictate the placement of smoke detectors, fire alarms, and fire extinguishers throughout the home. Floor plans must also include fire escape routes and ensure that all rooms have adequate access to exits.
- Structural safety: Structural safety codes ensure that the home is designed and built to withstand the loads and forces it will be subjected to, such as wind, snow, and earthquakes. Floor plans must include details of the home’s foundation, framing, and other structural elements.
- Electrical safety: Electrical safety codes govern the design and installation of electrical systems in the home. Floor plans must include details of the home’s electrical wiring, outlets, and fixtures.
- Plumbing safety: Plumbing safety codes govern the design and installation of plumbing systems in the home. Floor plans must include details of the home’s water supply, drainage system, and fixtures.
By carefully considering code compliance and safety, homeowners and architects can create floor plans that are not only functional and aesthetically pleasing but also safe and secure.
In addition to building codes, homeowners and architects should also consider the safety of the home’s occupants when creating a floor plan. This includes:
- Universal design: Universal design features can make the home more accessible and safe for people of all ages and abilities. For example, wider doorways, ramps, and grab bars can make the home more accessible for people with disabilities.
- Crime prevention: Crime prevention features can help to deter crime and make the home safer. For example, good lighting, strong locks, and security systems can help to protect the home from intruders.
- Emergency preparedness: Floor plans should also consider emergency preparedness. For example, the home should have a designated safe room or shelter in place in case of a natural disaster or other emergency.
By carefully considering code compliance, safety, and the needs of the occupants, homeowners and architects can create floor plans that are not only functional and aesthetically pleasing but also safe and secure.
Energy efficiency and sustainability
Energy efficiency and sustainability are becoming increasingly important considerations in the design of new homes. Homeowners are looking for ways to reduce their energy consumption and environmental impact, and creating an energy-efficient floor plan is a great place to start.
There are a number of different ways to improve the energy efficiency of a house floor plan. One important factor is the orientation of the home. Homes that are oriented to take advantage of the sun’s natural heat can reduce their heating costs in the winter. For example, in the Northern Hemisphere, homes that are oriented to the south will receive the most sunlight. In the Southern Hemisphere, homes that are oriented to the north will receive the most sunlight.
Another important factor to consider is the placement of windows and doors. Windows and doors can be a major source of heat loss, so it is important to place them strategically. For example, windows should be placed on the south side of the home to take advantage of the sun’s heat. Doors should be placed on the north side of the home to minimize heat loss.
The size and shape of the home can also affect its energy efficiency. Smaller homes are generally more energy-efficient than larger homes. Homes with simple, rectangular shapes are also more energy-efficient than homes with complex, irregular shapes.
In addition to these general considerations, there are a number of specific features that can be incorporated into a house floor plan to improve its energy efficiency. These features include:
- Insulation: Insulation is one of the most important factors in reducing heat loss. Homes should be insulated in the attic, walls, and floors to minimize heat transfer.
- Energy-efficient windows and doors: Energy-efficient windows and doors are designed to reduce heat loss and gain. Look for windows and doors with high Energy Star ratings.
- Energy-efficient appliances: Energy-efficient appliances use less energy to operate. Look for appliances with the Energy Star label.
- Renewable energy sources: Renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and geothermal heat pumps, can be used to reduce the home’s reliance on fossil fuels.
By carefully considering energy efficiency and sustainability, homeowners and architects can create floor plans that are not only functional and aesthetically pleasing but also environmentally friendly and cost-effective.
Personal preferences and lifestyle
The personal preferences and lifestyle of the homeowners are key considerations when creating a house floor plan. The floor plan should reflect the way the homeowners live and the activities they enjoy. For example, a family with young children may want a floor plan with a large family room and a dedicated playroom. A couple who loves to entertain may want a floor plan with a formal dining room and a spacious living room. A homeowner who works from home may want a floor plan with a dedicated home office.
Here are some specific factors to consider when designing a floor plan that meets the personal preferences and lifestyle of the homeowners:
- Number of people and their ages: The number of people who will be living in the home and their ages will impact the size and layout of the floor plan. For example, a family with young children will need a floor plan with more bedrooms and bathrooms than a couple who is empty nesters.
- Lifestyle and activities: The homeowners’ lifestyle and activities will also impact the floor plan. For example, a family who loves to cook and entertain may want a floor plan with a large kitchen and dining room. A couple who loves to watch movies may want a floor plan with a dedicated media room.
- Hobbies and interests: The homeowners’ hobbies and interests can also be incorporated into the floor plan. For example, a homeowner who loves to garden may want a floor plan with a sunroom or greenhouse. A homeowner who loves to play music may want a floor plan with a dedicated music room.
- Future plans: The homeowners’ future plans should also be considered when creating a floor plan. For example, a couple who is planning to have children may want a floor plan with a flexible layout that can be easily adapted to accommodate a growing family.
By carefully considering the personal preferences and lifestyle of the homeowners, architects can create floor plans that are not only functional and aesthetically pleasing but also tailored to the specific needs of the homeowners.
In addition to the factors listed above, there are a number of other personal preferences and lifestyle choices that can impact the design of a house floor plan. These include:
- Design style: The homeowners’ design style will influence the overall look and feel of the floor plan. For example, a couple who prefers a modern design style may want a floor plan with clean lines and open spaces. A family who prefers a traditional design style may want a floor plan with more formal spaces and traditional details.
- Budget: The homeowners’ budget will also impact the design of the floor plan. For example, a couple with a limited budget may need to choose a smaller floor plan or make compromises on certain features.
- Lot size and orientation: The size and orientation of the lot will also impact the design of the floor plan. For example, a small lot may require a smaller floor plan or a more creative use of space.
By carefully considering all of these factors, homeowners and architects can create floor plans that are not only functional and aesthetically pleasing but also tailored to the specific needs and preferences of the homeowners.
Budget and cost-effectiveness
Budget and cost-effectiveness are important considerations when creating a house floor plan. The cost of building a home can vary significantly depending on the size, complexity, and materials used. By carefully planning the floor plan, homeowners can save money without sacrificing quality or functionality.
One of the most important factors to consider when budgeting for a new home is the size of the home. Larger homes generally cost more to build than smaller homes. However, it is important to choose a home size that meets the needs of the family. A home that is too small can be cramped and uncomfortable, while a home that is too large can be expensive to build and maintain.
Another important factor to consider is the complexity of the floor plan. Homes with complex floor plans, such as those with multiple stories or unusual shapes, can be more expensive to build than homes with simple floor plans. However, complex floor plans can also create more interesting and unique living spaces.
The materials used to build the home can also impact the cost. For example, homes built with high-quality materials, such as brick or stone, can be more expensive to build than homes built with less expensive materials, such as vinyl or aluminum siding.
By carefully considering the size, complexity, and materials used, homeowners can create a house floor plan that meets their needs and budget.
Here are some specific tips for creating a cost-effective house floor plan:
- Keep the floor plan simple: Complex floor plans can be more expensive to build than simple floor plans. Stick to a simple, rectangular shape and avoid unnecessary nooks and crannies.
- Use standard materials and finishes: Standard materials and finishes are less expensive than custom materials and finishes. Choose materials that are durable and easy to maintain.
- Maximize natural light: Natural light can reduce the need for artificial lighting, which can save money on energy bills. Place windows and doors strategically to take advantage of natural light.
- Consider energy efficiency: Energy-efficient features, such as insulation and energy-efficient appliances, can save money on energy bills over time. Incorporate energy-efficient features into the floor plan whenever possible.
By following these tips, homeowners can create a house floor plan that is not only functional and aesthetically pleasing but also cost-effective.










Related Posts