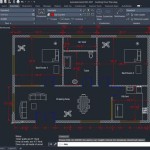
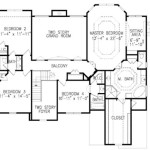
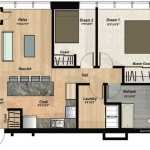
A floor plan drawing is a 2D diagram that depicts the layout of a room or structure from above. It illustrates the spatial relationships between walls, doors, windows, and other features, providing a concise overview of the interior or exterior space.
Floor plan drawings are essential in architecture, engineering, and interior design. Architects use them to design and visualize buildings, engineers to plan electrical and plumbing systems, and interior designers to arrange furniture and decor. By understanding the spatial layout of a space, individuals can make informed decisions regarding construction, renovations, or design choices.
Floor plan drawing software and applications enable architects and designers to create detailed and accurate plans. These digital tools allow for precise measurements, easy modifications, and the incorporation of furnishings and fixtures. As such, they streamline the design process and facilitate collaboration among professionals.
Floor plan drawings are fundamental in architecture and design. Here are nine important points to consider:
- Precise measurements
- Accurate scale
- Clear symbols and notations
- Proper labeling
- North arrow orientation
- Furniture and fixtures placement
- Wall dimensions and openings
- Room areas and dimensions
- Adherence to building codes
By incorporating these elements, floor plan drawings become valuable tools for architects, engineers, and interior designers.
Precise measurements
Precise measurements are crucial in floor plan drawings. Accurate dimensions ensure that the plan is a true representation of the space and that construction or renovations can be carried out accordingly. Measurements should be taken from a fixed reference point and include the following:
- Overall dimensions of the space
This includes the length, width, and height of the room or structure. - Wall lengths and heights
Measurements should be taken for each wall, including any recesses or protrusions. - Door and window dimensions
Indicate the height and width of all doors and windows, as well as their location within the walls. - Distances between features
Measure the distance between walls, doors, windows, and other significant features, such as fireplaces or built-in cabinets.
Precise measurements allow architects, engineers, and interior designers to create plans that are accurate and functional. They ensure that the final construction or renovation project aligns with the intended design and meets building codes and regulations.
Accurate scale
Accurate scale is essential in floor plan drawings. It ensures that the plan is a true representation of the space and that measurements are consistent throughout. When choosing a scale, architects and designers must consider the size of the space and the level of detail required.
- Common scales for floor plans
Common scales used for floor plans include 1:50, 1:100, and 1:200. A scale of 1:50 means that one unit on the drawing represents 50 units in real life. This scale is suitable for small spaces, such as apartments or single-family homes. - Choosing the right scale
The appropriate scale for a floor plan depends on the size of the space and the level of detail required. Larger spaces, such as commercial buildings or warehouses, may require a smaller scale, such as 1:200, to fit the entire plan on a single sheet. Smaller spaces, such as residential units, can use a larger scale, such as 1:50, to show more detail. - Maintaining scale throughout the drawing
It is important to maintain the chosen scale throughout the floor plan drawing. All measurements and dimensions should be consistent, and objects should be drawn in proportion to their actual size. This ensures that the plan is accurate and easy to interpret. - Using a scale bar
A scale bar is a graphical representation of the scale used in a floor plan drawing. It allows users to quickly and easily determine the actual dimensions of objects on the plan. Scale bars are typically placed in a corner of the drawing and indicate the distance represented by a specific length on the plan.
Accurate scale is a fundamental aspect of floor plan drawings. By choosing the right scale and maintaining consistency throughout the drawing, architects and designers can create plans that are precise, informative, and easy to understand.
Clear symbols and notations
Clear symbols and notations are essential in floor plan drawings to convey information concisely and accurately. They provide a standardized language that allows architects, engineers, and interior designers to communicate design intent and construction details effectively.
Symbols are used to represent various elements of a floor plan, such as walls, doors, windows, furniture, and fixtures. Each symbol is carefully designed to convey specific information about the element it represents. For example, a solid line typically represents a wall, while a dashed line may indicate a door or window opening. Furniture symbols are often simplified representations of the actual furniture pieces, indicating their size, shape, and placement.
Notations are used to provide additional information about the elements in a floor plan. They can include dimensions, materials, finishes, and other relevant details. Notations are typically placed near the symbol they refer to and are written in a clear and concise manner. For example, a notation next to a wall symbol may indicate the wall’s thickness or construction type.
Using clear symbols and notations ensures that floor plan drawings are easy to understand and interpret. They allow architects, engineers, and interior designers to communicate their design ideas and construction requirements accurately and efficiently.
Proper labeling
Proper labeling is essential in floor plan drawings to ensure clear and accurate communication of design intent and construction details. Labels provide information about the various elements of a floor plan, such as rooms, spaces, walls, doors, windows, and fixtures. They help users identify and understand the purpose and function of each element, making the drawing easier to interpret and use.
- Room and space labels
Room and space labels identify the different rooms and spaces within a floor plan. They are typically written in all capital letters and placed within the respective room or space. For example, a label might read “LIVING ROOM” or “BEDROOM 1”.
- Wall labels
Wall labels provide information about the walls in a floor plan, including their thickness, material, and construction type. They are typically written in a smaller font and placed near the wall they refer to. For example, a label might read “6” WALL” to indicate a 6-inch thick wall.
- Door and window labels
Door and window labels identify the different doors and windows in a floor plan. They typically include the type of door or window, such as “SINGLE DOOR” or “DOUBLE WINDOW”, as well as its dimensions. The labels are usually placed near the door or window they refer to.
- Fixture labels
Fixture labels identify the different fixtures in a floor plan, such as sinks, toilets, bathtubs, and appliances. They are typically written in a smaller font and placed near the fixture they refer to. For example, a label might read “SINK” or “REFRIGERATOR”.
Proper labeling ensures that floor plan drawings are clear, informative, and easy to understand. It allows architects, engineers, and interior designers to communicate their design ideas and construction requirements accurately and efficiently.
North arrow orientation
North arrow orientation is crucial in floor plan drawings as it provides a reference point for understanding the spatial layout and the direction of the building or space. It helps architects, engineers, and interior designers accurately plan the placement of rooms, windows, and other elements to optimize natural light, ventilation, and overall functionality.
- Accurate placement of building elements
By aligning the floor plan with the cardinal directions, architects can ensure that building elements such as windows, doors, and skylights are positioned to take advantage of natural light and ventilation. For example, placing windows facing south maximizes sunlight exposure, while orienting them towards prevailing winds promotes natural ventilation.
- Site planning and landscaping
North arrow orientation is essential for site planning and landscaping. It helps determine the optimal placement of the building on the site, considering factors such as solar orientation, prevailing wind patterns, and views. By aligning the building with the cardinal directions, architects can create outdoor spaces that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
- Building codes and regulations
In many jurisdictions, building codes and regulations require floor plans to include a north arrow for accurate building permit submissions. This is because the orientation of a building can impact various aspects of construction, such as structural design, energy efficiency, and compliance with zoning laws.
- Wayfinding and accessibility
North arrow orientation aids in wayfinding and accessibility within a building or space. By providing a clear reference point, it helps users orient themselves and navigate through the floor plan, especially in large or complex structures.
Proper north arrow orientation in floor plan drawings ensures accuracy, functionality, and compliance with building codes and regulations. It empowers architects, engineers, and interior designers to create well-planned and efficient spaces that meet the needs of occupants and adhere to industry standards.
Furniture and fixtures placement
Furniture and fixtures play a crucial role in the functionality and aesthetics of a space. In floor plan drawings, careful consideration is given to the placement of these elements to maximize space utilization, improve flow, and create a visually pleasing environment.
- Space planning and functionality
Furniture and fixtures should be arranged to optimize space utilization and ensure smooth flow of movement within the space. This involves considering the size and shape of the furniture, as well as the intended use of the space. For example, in a living room, seating should be arranged to facilitate conversation and entertainment, while in a kitchen, the placement of appliances and cabinets should allow for efficient meal preparation.
- Ergonomics and accessibility
Furniture and fixtures should be placed to promote ergonomic principles and accessibility. This means ensuring that furniture is comfortable to use, reduces strain, and allows for easy access to all areas of the space. For example, desks and chairs should be positioned to support good posture, while hallways and doorways should be wide enough for wheelchair accessibility.
- Focal points and visual interest
Furniture and fixtures can be used to create focal points and add visual interest to a space. A strategically placed statement piece, such as a large sofa or an eye-catching artwork, can draw attention and create a sense of balance. Additionally, the arrangement of furniture and fixtures can create visual flow and guide the eye through the space.
- Scale and proportion
The scale and proportion of furniture and fixtures should be carefully considered in relation to the size of the space. Oversized furniture in a small room can make the space feel cramped and uncomfortable, while undersized furniture in a large room can appear insignificant and lost. By selecting furniture and fixtures that are appropriately scaled to the space, a sense of harmony and balance can be achieved.
Proper furniture and fixtures placement enhances the functionality, aesthetics, and overall user experience of a space. By carefully considering the principles of space planning, ergonomics, visual appeal, and scale, architects and interior designers can create floor plan drawings that optimize the use of space and create inviting and comfortable environments.
Wall dimensions and openings
Wall dimensions and openings are crucial elements in floor plan drawings as they define the spatial layout and functionality of a space. Accurate representation of wall dimensions and openings is essential for construction, renovation, and interior design projects.
Wall dimensions
Wall dimensions include the length, height, and thickness of walls. These dimensions are critical for determining the overall size of the space, as well as the placement of doors, windows, and other openings. Accurate wall dimensions ensure that the floor plan is a true representation of the actual space, allowing for precise construction and material estimation.
Door openings
Door openings are represented in floor plan drawings by lines indicating the swing direction of the door. The dimensions of door openings include the width and height of the opening, as well as the location of the door within the wall. Door openings should be carefully planned to ensure proper flow of movement and accessibility throughout the space.
Window openings
Window openings are represented in floor plan drawings by symbols that indicate the type and size of the window. The dimensions of window openings include the width and height of the opening, as well as the location of the window within the wall. Window openings should be strategically placed to maximize natural light and ventilation, while also considering factors such as privacy and energy efficiency.
Room areas and dimensions
Room areas and dimensions are crucial aspects of floor plan drawings as they provide essential information about the size and proportions of each space within a building or structure. Accurate representation of room areas and dimensions is vital for space planning, construction, and interior design.
Overall room dimensions
Overall room dimensions include the length, width, and height of a room. These dimensions determine the overall size and volume of the space and are used to calculate the square footage or square meterage of the room. Accurate overall room dimensions are essential for space planning and determining the appropriate furniture and fixtures for the space.
Room area calculations
Room area calculations are based on the overall room dimensions. The area of a room is typically calculated by multiplying the length by the width. In some cases, such as rooms with irregular shapes, the area may need to be calculated using more complex methods. Accurate room area calculations are important for determining the amount of flooring, paint, or other materials needed for construction or renovation projects.
Room proportions
Room proportions refer to the relationship between the length, width, and height of a room. Well-proportioned rooms are aesthetically pleasing and create a sense of balance and harmony. Architects and interior designers use room proportions to create spaces that are both functional and visually appealing. For example, a room with equal length and width is considered a square proportion, which is often used in formal settings, while a room with a longer length than width is considered a rectangular proportion, which is commonly used in living rooms and bedrooms.
Code and regulation compliance
Room areas and dimensions may also need to comply with building codes and regulations. These codes and regulations may specify minimum room sizes for certain types of spaces, such as bedrooms, bathrooms, and kitchens. Ensuring that room areas and dimensions meet code requirements is essential for obtaining building permits and ensuring the safety and habitability of the space.
Accurate and detailed room areas and dimensions are essential for effective floor plan drawings. They provide valuable information for architects, engineers, interior designers, and contractors to create functional, aesthetically pleasing, and code-compliant spaces.
Adherence to building codes
Building codes are regulations and standards established by local authorities to ensure the safety, structural integrity, and habitability of buildings and structures. Floor plan drawings must adhere to these building codes to ensure compliance with legal requirements and to protect the health and well-being of occupants.
Structural safety
Building codes specify minimum requirements for structural elements, such as walls, beams, and foundations, to ensure that buildings can withstand various loads and forces, including gravity, wind, and earthquakes. Floor plan drawings must accurately represent the structural components of the building and demonstrate that they meet or exceed the code requirements. This ensures the structural stability and safety of the building.
Fire safety
Building codes include regulations for fire safety measures, such as fire-rated walls, smoke detectors, and fire sprinkler systems. Floor plan drawings must indicate the location and type of fire safety features and demonstrate that the building complies with the code requirements. This helps prevent the spread of fire and protects occupants in the event of a fire.
Accessibility
Building codes mandate accessibility features to ensure that buildings are accessible to individuals with disabilities. Floor plan drawings must show accessible routes, ramps, elevators, and other features that comply with the code requirements. This ensures that people with disabilities can safely and independently access and use the building.
Sustainability
Some building codes include sustainability requirements to promote energy efficiency and environmental protection. Floor plan drawings must demonstrate how the building meets these requirements, such as by incorporating energy-efficient appliances, insulation, and natural lighting. Adherence to sustainability codes reduces the environmental impact of the building and lowers operating costs.










Related Posts