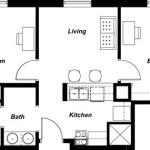
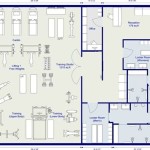
Floor Plans Timber Frame refers to detailed plans that guide the construction of timber-framed floors, providing a structural framework for buildings. These plans outline the placement, dimensions, and connections of timber beams, joists, and other supporting elements, ensuring a stable and durable foundation for the structure.
In practice, floor plans timber frame play a crucial role in residential, commercial, and industrial constructions. They enable architects, engineers, and builders to visualize and precisely execute the floor framing, which is essential for load-bearing capacity, floor layout, and overall building integrity. For instance, in a residential home, a well-designed floor plan timber frame ensures a safe and sound foundation for the living spaces, distributing weight effectively and providing a solid base for walls, ceilings, and other structural components.
To delve deeper into the intricacies of floor plans timber frame, let’s explore the key components and considerations involved in their design and execution.
Floor plans timber frame encompass various important considerations that contribute to their effectiveness and structural integrity. Here are eight key points to remember:
- Precise Measurements: Accuracy in dimensions is paramount for proper fitting and load distribution.
- Beam Sizing: Choosing the correct beam size ensures load-bearing capacity and minimizes deflection.
- Joist Spacing: Proper spacing of joists provides adequate support for flooring and prevents sagging.
- Connection Details: Strong and durable connections between beams and joists are crucial for overall stability.
- Openings for Utilities: Plans should accommodate openings for plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems.
- Fire Resistance: Fire-retardant materials and design features can enhance the structure’s fire safety.
- Sustainability: Using sustainable timber sources and efficient designs promotes environmental responsibility.
- Professional Expertise: Involving qualified architects and engineers ensures adherence to building codes and industry best practices.
Considering these points during the design and execution of floor plans timber frame helps ensure the structural soundness, safety, and longevity of the building.
Precise Measurements: Accuracy in dimensions is paramount for proper fitting and load distribution.
In floor plans timber frame, precise measurements play a pivotal role in ensuring the structural integrity and overall stability of the building. Accuracy in dimensions is crucial for several reasons:
- Proper Fitting: Precise measurements ensure that all timber components, including beams, joists, and other framing members, fit together seamlessly. This proper fitting eliminates gaps and misalignments, preventing structural weaknesses and ensuring a secure and stable framework.
- Load Distribution: Accurate dimensions are essential for distributing loads effectively throughout the floor structure. Proper load distribution prevents overloading of certain areas, which could lead to structural failure. Precise measurements ensure that each component carries its intended load, minimizing the risk of sagging, deflection, or collapse.
- Efficient Use of Materials: Precise measurements minimize material waste and optimize the use of timber. Accurate plans reduce the likelihood of errors during cutting and assembly, ensuring that materials are utilized efficiently. This not only saves costs but also promotes sustainability by reducing unnecessary material consumption.
- Compliance with Building Codes: Building codes often specify minimum dimensions and load-bearing capacities for floor framing. Precise measurements ensure compliance with these codes, guaranteeing the safety and structural integrity of the building. Accurate plans help avoid costly rework or structural deficiencies that could compromise the building’s safety.
Overall, precise measurements in floor plans timber frame are fundamental for proper fitting, efficient load distribution, optimal material utilization, and compliance with building codes. They lay the foundation for a sturdy, safe, and durable timber-framed structure.
Beam Sizing: Choosing the correct beam size ensures load-bearing capacity and minimizes deflection.
In floor plans timber frame, beam sizing is a critical consideration that directly impacts the structural integrity and performance of the floor system. Selecting the correct beam size is essential for ensuring adequate load-bearing capacity and minimizing deflection.
Load-Bearing Capacity: Beams are the primary load-bearing elements in a timber-framed floor. They carry the weight of the structure above, including walls, ceilings, furniture, and occupants. The size of the beams must be sufficient to withstand these loads safely and prevent collapse. Structural engineers use calculations and industry standards to determine the appropriate beam size based on the span of the beam, the spacing of the beams, and the expected loads.
Deflection: Deflection refers to the bending or sagging of beams under load. Excessive deflection can compromise the stability of the floor and cause structural damage. Choosing the correct beam size helps minimize deflection by ensuring that the beams have adequate stiffness to resist bending. Factors such as the length of the beam, the modulus of elasticity of the timber, and the applied load influence the deflection of a beam.
Factors Affecting Beam Size: Several factors influence the selection of beam size in floor plans timber frame:
- Span of the Beam: The longer the beam, the larger the size required to support the same load.
- Spacing of the Beams: Closer spacing of beams allows for smaller beam sizes, as the load is distributed over more beams.
- Species of Timber: Different timber species have varying strengths and stiffness, whichs the required beam size.
- Grade of Timber: The grade of timber indicates its strength and quality. Higher-grade timber allows for smaller beam sizes.
- Live Loads and Dead Loads: Live loads (occupants, furniture) and dead loads (permanent structural elements) must be considered when determining beam size.
Choosing the correct beam size is crucial for ensuring a safe and functional timber-framed floor. Structural engineers carefully consider all relevant factors to determine the optimal beam size for each application.
Joist Spacing: Proper spacing of joists provides adequate support for flooring and prevents sagging.
In floor plans timber frame, joist spacing plays a crucial role in ensuring the structural integrity and performance of the floor system. Proper spacing of joists provides adequate support for the flooring and prevents excessive deflection or sagging.
Load Distribution: Joists are horizontal framing members that span between beams and support the flooring. Proper spacing ensures that the load from the flooring is distributed evenly across the joists. This prevents overloading of individual joists, which could lead to structural failure. The spacing of joists is determined based on the thickness and strength of the flooring material, as well as the expected loads.
Deflection Control: Deflection refers to the bending or sagging of joists under load. Excessive deflection can compromise the stability of the floor and cause damage to the flooring. Proper joist spacing helps minimize deflection by ensuring that the joists are close enough together to provide adequate support for the flooring. Factors such as the span of the joists, the species of timber, and the grade of timber influence the deflection of a joist.
Floor Stiffness: The stiffness of a floor refers to its resistance to bending or deflection. Proper joist spacing contributes to the overall stiffness of the floor by providing more support points for the flooring. This increased stiffness improves the floor’s ability to loads and reduces the likelihood of excessive deflection.
Choosing the correct joist spacing is essential for ensuring a safe and functional timber-framed floor. Structural engineers carefully consider all relevant factors to determine the optimal joist spacing for each application.
Connection Details: Strong and durable connections between beams and joists are crucial for overall stability.
In floor plans timber frame, connection details refer to the methods and techniques used to join beams and joists together. Strong and durable connections are essential to ensure the overall stability and structural integrity of the floor system. Proper connections transfer loads effectively between members, prevent joint failure, and maintain the alignment of the framing.
- Bolted Connections: Bolts are commonly used to connect beams and joists. High-strength bolts are inserted through pre-drilled holes in the members and tightened to create a secure joint. Bolted connections provide strong and reliable load transfer and can be easily inspected and maintained.
- Nailed Connections: Nails are another common method for connecting beams and joists. Structural nails are specifically designed for timber framing and provide a cost-effective and efficient way to create strong joints. However, nailed connections may be susceptible to loosening over time and require periodic inspection and reinforcement.
- Joist Hangers: Joist hangers are metal brackets that are nailed or bolted to the beam and joist. They provide support for the joists and help distribute loads. Joist hangers are particularly useful when connecting joists to beams of different sizes or when the joists are not directly above the beams.
- Timber Connectors: Timber connectors are specialized metal plates or devices that are used to connect beams and joists. They provide increased strength and rigidity to the joint and are often used in high-load applications or in areas where there are complex forces acting on the structure.
Choosing the appropriate connection details for floor plans timber frame depends on various factors such as the load requirements, the type of timber used, and the overall design of the structure. Structural engineers carefully consider these factors to ensure that the connections are strong enough to withstand the anticipated loads and maintain the structural integrity of the floor system.
Openings for Utilities: Plans should accommodate openings for plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems.
In floor plans timber frame, it is crucial to incorporate openings for utilities such as plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems. These openings allow for the seamless integration of essential services into the structure, ensuring the functionality and comfort of the building.
- Plumbing Openings: Floor plans should include designated openings for plumbing pipes and fixtures. These openings allow for the installation of water supply lines, drain pipes, and sanitary fixtures, such as sinks, toilets, and bathtubs. Proper planning of plumbing openings ensures efficient water distribution and drainage throughout the building.
- Electrical Openings: Floor plans must accommodate openings for electrical wiring and outlets. These openings allow for the installation of electrical circuits, switches, and outlets, providing power and lighting to the building. Proper placement of electrical openings ensures convenient access to electricity and minimizes the need for unsightly extension cords.
- HVAC Openings: Floor plans should include provisions for HVAC systems, including heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. These openings allow for the installation of ductwork, vents, and registers, ensuring the distribution of conditioned air throughout the building. Proper planning of HVAC openings promotes a comfortable indoor environment and improves energy efficiency.
- Coordination with Contractors: The planning of openings for utilities requires close coordination with plumbing, electrical, and HVAC contractors. These contractors provide valuable input on the location and size of openings, ensuring that they align with the specific requirements of the utility systems being installed.
By incorporating openings for utilities into floor plans timber frame, architects and engineers ensure the smooth integration of essential services into the building. This proactive planning avoids costly rework or retrofitting during construction and enhances the overall functionality and livability of the structure.
Fire Resistance: Fire-retardant materials and design features can enhance the structure’s fire safety.
Incorporating fire resistance into floor plans timber frame is crucial for ensuring the safety of occupants and minimizing property damage in the event of a fire. Fire-retardant materials and thoughtful design features can significantly enhance the structure’s ability to withstand and contain fire, providing valuable time for evacuation and firefighting efforts.
- Fire-Retardant Timber: Using fire-retardant treated timber is a key strategy to improve the fire resistance of timber-framed floors. This treatment involves impregnating the timber with chemicals that slow down the spread of flames and reduce smoke production. Fire-retardant timber can significantly extend the time it takes for the timber to ignite and burn, providing more time for occupants to escape and firefighters to respond.
- Fire-Resistant Barriers: Incorporating fire-resistant barriers, such as gypsum board or mineral wool, into the floor structure can help contain a fire within a specific area. These barriers act as a protective layer, preventing the spread of flames and smoke through gaps and openings. By compartmentalizing the structure, fire-resistant barriers help prevent the fire from engulfing the entire building.
- Compartmentalization: Compartmentalization involves dividing the floor plan into smaller sections using fire-resistant walls and doors. This design strategy limits the spread of fire and smoke by creating physical barriers. In the event of a fire, compartmentalization allows occupants to evacuate safely from one section to another, increasing their chances of survival.
- Fire-Rated Assemblies: Using fire-rated assemblies, such as fire-rated doors and windows, is essential for maintaining the integrity of fire-resistant barriers. These assemblies are designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire and smoke through openings in walls and floors. By incorporating fire-rated assemblies, the structure’s ability to contain a fire is significantly improved.
By incorporating fire-resistant materials and design features into floor plans timber frame, architects and engineers can enhance the structure’s fire safety, protect occupants, and minimize the risk of catastrophic damage in the event of a fire.
Sustainability: Using sustainable timber sources and efficient designs promotes environmental responsibility.
Sustainability is a key consideration in modern construction practices, and floor plans timber frame are no exception. By incorporating sustainable practices, architects and engineers can minimize the environmental impact of timber-framed structures while promoting responsible resource management.
- Sustainable Timber Sourcing:
Using timber from sustainably managed forests is essential for preserving natural resources and promoting biodiversity. Sustainable forestry practices ensure that trees are harvested at a rate that allows the forest to regenerate naturally, while also protecting wildlife habitats and water quality.
- Efficient Design:
Efficient floor plan designs can reduce the amount of timber required for construction, minimizing material waste and preserving resources. Optimizing the use of space, employing innovative framing techniques, and incorporating natural light can all contribute to a more sustainable design.
- Recycled and Reused Timber:
Incorporating recycled or reused timber into the floor framing can further reduce the environmental impact. Using reclaimed wood from old structures or utilizing byproducts from other industries diverts waste from landfills and promotes a circular economy.
- Low-VOC Materials:
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are harmful chemicals that can be emitted from certain building materials. Using low-VOC materials, such as eco-friendly adhesives and finishes, helps to improve indoor air quality and reduce the environmental impact of the structure.
By adopting sustainable practices in floor plans timber frame, architects and engineers can create environmentally responsible structures that promote the well-being of both occupants and the planet.
Professional Expertise: Involving qualified architects and engineers ensures adherence to building codes and industry best practices.
Engaging qualified architects and engineers in the design and execution of floor plans timber frame is crucial for ensuring the structural integrity, safety, and compliance of the building. Their expertise is essential in navigating building codes, implementing industry best practices, and delivering a well-designed and functional structure.
- Code Compliance:
Architects and engineers are well-versed in the relevant building codes and regulations, which vary depending on the jurisdiction. They ensure that the floor plans timber frame are designed and constructed in accordance with these codes, meeting minimum safety and structural requirements. This compliance minimizes the risk of costly code violations, construction delays, and potential legal liabilities.
- Structural Integrity:
Qualified engineers possess the technical knowledge and experience to analyze and design floor plans timber frame that are structurally sound and able to withstand the anticipated loads and forces. They consider factors such as the weight of the building, wind loads, seismic activity, and other potential hazards to ensure the stability and longevity of the structure.
- Efficient Design:
Architects play a vital role in creating efficient and functional floor plans timber frame. They optimize the use of space, minimize material waste, and incorporate sustainable design principles. Their expertise helps achieve a well-organized and aesthetically pleasing layout that meets the specific needs and preferences of the occupants.
- Constructability:
Engineers and architects collaborate to ensure that the floor plans timber frame are constructible and practical to build. They consider factors such as the availability of materials, construction methods, and sequencing. Their expertise helps minimize potential construction challenges, reducing the risk of delays, cost overruns, and safety hazards.
By involving qualified architects and engineers in floor plans timber frame, building owners and developers can be confident that their structures are designed and built to the highest standards of safety, code compliance, efficiency, and constructability.









Related Posts