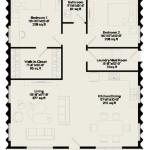
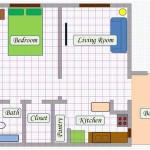
A “House Plan 2nd Floor” is a concept in architecture referring specifically to the plan or layout of the second story of a house. It serves as a blueprint that guides the construction of the upper level, including the arrangement of rooms, hallways, stairs, bathrooms, and other essential spaces.
In real-world applications, House Plan 2nd Floor layouts are crucial in optimizing the functionality and livability of a home. They ensure the efficient use of space, provide a framework for electrical and plumbing systems, and contribute significantly to the overall aesthetic appeal of the structure.
Moving forward, we will delve into the key considerations and best practices associated with designing and planning a House Plan 2nd Floor, exploring its various elements and the factors that influence its design.
When designing a House Plan 2nd Floor, several important points require careful consideration:
- Room arrangement
- Space allocation
- Traffic flow
- Natural lighting
- Ventilation
- Electrical planning
- Plumbing placement
- Structural integrity
Balancing these elements effectively ensures a functional, comfortable, and aesthetically pleasing living space on the second floor.
Room arrangement
Room arrangement on the second floor of a house plan is crucial for creating a functional and comfortable living space. It involves carefully positioning and sizing rooms to ensure efficient use of space, smooth traffic flow, and optimal natural lighting.
- Master suite placement: The master suite, typically the largest and most private room on the second floor, should be situated in a quiet corner of the house, away from high-traffic areas like the stairs or family room. It should also have access to a private bathroom and, if possible, a walk-in closet.
- Secondary bedrooms: Secondary bedrooms should be grouped together, creating a dedicated sleeping area for children or guests. These rooms should be sized appropriately for their intended use and have adequate closet space.
- Bathroom placement: Bathrooms should be conveniently located near bedrooms, avoiding long and awkward trips down the hall. A full bathroom, with a bathtub or shower and toilet, should be accessible from the master suite. Additional bathrooms can be shared between secondary bedrooms.
- Common areas: Common areas on the second floor, such as a family room or loft, should be placed centrally, providing easy access from different rooms. These spaces should be designed to accommodate various activities, from relaxation to entertainment.
By carefully considering room arrangement, homeowners can create a second-floor plan that meets their specific needs and preferences, fostering a comfortable and enjoyable living environment.
Space allocation
Space allocation on the second floor of a house plan plays a crucial role in determining the functionality and livability of the space. It involves carefully distributing the available square footage among different rooms and areas to ensure optimal use and a comfortable living environment.
- Master suite: The master suite, comprising the bedroom, bathroom, and walk-in closet, typically requires the most space on the second floor. It should be designed to provide a sense of privacy and luxury, with ample room for a king-size bed, seating area, and storage.
- Secondary bedrooms: Secondary bedrooms should be allocated space based on their intended use and the number of occupants. A child’s bedroom may require less space than a guest room, while a room intended for multiple children may need additional square footage.
- Bathrooms: Bathrooms should be designed to be spacious and functional, with adequate room for fixtures, storage, and comfortable movement. The size of the bathroom will depend on the number of fixtures and the overall layout of the second floor.
- Common areas: Common areas on the second floor, such as a family room or loft, should be allocated space based on the anticipated activities and the number of people who will be using the space. These areas should be large enough to accommodate furniture, seating, and any other necessary amenities.
By carefully considering space allocation, homeowners can create a second-floor plan that meets their specific needs and preferences, ensuring a comfortable and enjoyable living space.
Traffic flow
Traffic flow on the second floor of a house plan is crucial for creating a functional and comfortable living space. It involves carefully planning the arrangement of rooms and hallways to ensure smooth and efficient movement throughout the floor.
- Clear pathways: All rooms and areas on the second floor should be easily accessible via clear and well-defined pathways. Hallways should be wide enough to accommodate comfortable movement, and doorways should be placed to avoid creating bottlenecks.
- Centralized access: Common areas, such as the family room or loft, should be centrally located to provide easy access from different rooms. This minimizes the need for residents to navigate through multiple hallways or rooms to reach the desired destination.
- Private circulation: The master suite and secondary bedrooms should have dedicated hallways or access points to maintain privacy and minimize disturbance from other areas of the second floor.
- Staircase placement: The staircase leading to the second floor should be conveniently located and well-lit. It should not obstruct traffic flow or create awkward transitions between floors.
By carefully considering traffic flow, homeowners can create a second-floor plan that promotes easy movement, reduces congestion, and enhances the overall functionality and livability of the space.
Natural lighting
Natural lighting is crucial for creating a comfortable and inviting living space on the second floor of a house. It involves strategically placing windows and skylights to maximize the amount of natural light entering the rooms, reducing the need for artificial lighting and creating a connection to the outdoors.
- Window placement: Windows should be placed on walls that face south or west to take advantage of natural light throughout the day. Larger windows or multiple windows in a room can provide ample illumination and create a sense of spaciousness.
- Skylights: Skylights are an excellent way to introduce natural light into rooms that may not have access to exterior walls. They can be placed above hallways, bathrooms, or closets, bringing light into areas that would otherwise be dark and enclosed.
- Light shelves: Light shelves are horizontal surfaces placed above windows that reflect natural light deeper into a room. They can be used to distribute light more evenly and reduce the need for artificial lighting in the center of a room.
- Clerestory windows: Clerestory windows are tall, narrow windows placed high on a wall, near the ceiling. They allow natural light to enter a room without compromising privacy or creating excessive heat gain.
By carefully considering natural lighting, homeowners can create a second-floor plan that is filled with natural light, reducing energy consumption, enhancing mood, and creating a healthier and more enjoyable living environment.
Ventilation
Ventilation on the second floor of a house plan is crucial for maintaining good indoor air quality, removing pollutants, and creating a comfortable living environment. It involves incorporating features that allow for the circulation of fresh air and the removal of stale air.
- Windows and doors: Windows and doors are essential for natural ventilation, allowing fresh air to enter and stale air to escape. They should be placed strategically to create cross-ventilation, where air can flow freely through the space.
- Exhaust fans: Exhaust fans in bathrooms and kitchens help to remove moisture, odors, and pollutants from the air. They should be vented directly to the outside to ensure effective removal of stale air.
- Ceiling fans: Ceiling fans can improve air circulation and provide a cooling effect in warmer months. They help to distribute air evenly throughout the room, reducing stratification and creating a more comfortable environment.
- Mechanical ventilation: In some cases, mechanical ventilation systems may be necessary to provide adequate ventilation on the second floor. These systems use ducts and fans to circulate air throughout the house, ensuring a constant supply of fresh air.
By carefully considering ventilation, homeowners can create a second-floor plan that promotes good indoor air quality, reduces the risk of moisture and mold problems, and enhances the overall comfort and health of the occupants.
Electrical planning
Electrical planning for the second floor of a house involves carefully considering the placement of electrical outlets, switches, and lighting fixtures to ensure adequate power, safety, and functionality throughout the space.
- Lighting: Lighting on the second floor should be planned to provide both ambient and task lighting. Ambient lighting, such as ceiling lights or chandeliers, provides general illumination, while task lighting, such as bedside lamps or under-cabinet lighting in bathrooms, focuses light on specific areas.
- Outlets: Electrical outlets should be placed conveniently throughout the second floor to accommodate various appliances and devices. Outlets should be placed near beds, desks, and seating areas, as well as in bathrooms, closets, and hallways.
- Switches: Light switches should be placed at all entrances to rooms and at the top and bottom of stairs for ease of use. Three-way switches, which allow a light to be controlled from two different locations, can be useful for larger rooms or hallways.
- Dedicated circuits: Dedicated circuits should be used for high-power appliances, such as air conditioners, refrigerators, and electric stoves. These circuits provide a dedicated power supply to prevent overloading and potential electrical hazards.
By carefully considering electrical planning, homeowners can ensure that the second floor of their house has adequate power, safety, and functionality, enhancing the comfort and convenience of the living space.
Plumbing placement
Plumbing placement on the second floor of a house plan involves carefully considering the location of fixtures, pipes, and drains to ensure efficient water supply and drainage throughout the space.
Bathrooms: Bathrooms are typically the most plumbing-intensive areas on the second floor. The placement of toilets, sinks, showers, and bathtubs should be carefully planned to optimize space utilization and minimize the length of plumbing runs. Back-to-back bathroom layouts, where bathrooms are positioned directly above each other, can simplify plumbing installation and reduce costs.
Kitchen: If the second floor includes a kitchen or kitchenette, the placement of the sink, dishwasher, and refrigerator should be carefully considered. Plumbing lines for these fixtures should be routed efficiently to minimize the distance between the fixtures and the main water supply and drain lines.
Laundry room: If a laundry room is located on the second floor, the placement of the washer and dryer should be planned to ensure close proximity to both the water supply and drain lines. A dedicated laundry sink can also be included for added convenience.
By carefully considering plumbing placement, homeowners can ensure that the second floor of their house has efficient water supply and drainage, reducing the risk of leaks, clogs, and other plumbing issues.
Structural integrity
Structural integrity is paramount in ensuring that the second floor of a house plan is safe and stable. It involves carefully considering the materials used, the design of the framing system, and the overall load-bearing capacity of the structure.
The framing system, typically composed of wood or steel, provides the primary support for the second floor. The design of the framing system should take into account the size and shape of the floor plan, as well as the anticipated loads that will be placed on the floor, such as furniture, occupants, and potential snow or wind loads. Beams and joists, the primary structural members of the framing system, should be sized and spaced appropriately to ensure adequate strength and rigidity.
The choice of materials used in the construction of the second floor also impacts its structural integrity. Wood is a common choice for framing, due to its strength, availability, and ease of use. Steel framing, while more expensive, offers greater strength and fire resistance. The selection of materials should be based on the specific requirements of the project and the desired level of structural performance.
In addition to the framing system and materials, the overall design of the second floor should also consider factors that affect structural integrity. For example, large open spaces or vaulted ceilings can require additional structural support to maintain stability. Proper detailing at connections between different structural elements is crucial to ensure that loads are transferred effectively and that the structure remains stable under various loading conditions.
By carefully considering structural integrity, homeowners can ensure that the second floor of their house is safe, stable, and able to withstand the anticipated loads and stresses it will encounter throughout its lifespan.









Related Posts