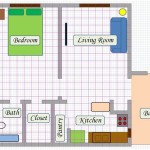
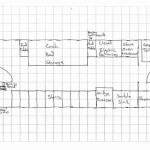
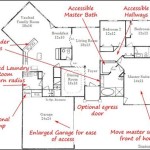
Second Floor Addition Plans are architectural blueprints that outline the construction of an additional level to an existing building. These plans provide detailed instructions on the layout, materials, and structural components required to create a new floor. Second Floor Addition Plans are commonly used to expand the living space of a home, add additional bedrooms or bathrooms, or create a dedicated home office or studio.
Before embarking on a second floor addition project, carefully consider the existing structure’s capacity to support the added weight, as well as local zoning regulations and building codes. Hiring a licensed architect or contractor to design and oversee the addition is crucial to ensure the structural integrity and safety of the project. Well-crafted Second Floor Addition Plans are essential for a successful and hassle-free renovation, providing a clear roadmap for builders and ensuring a finished product that meets your specific needs and expectations.
In the following sections, we will delve into the key elements and considerations involved in creating Second Floor Addition Plans. We will discuss factors such as structural engineering, material selection, space planning, and design aesthetic to guide you through the planning and execution of your second floor addition project.
When creating Second Floor Addition Plans, several key points should be considered to ensure a successful project:
- Structural Integrity
- Zoning Compliance
- Building Codes
- Material Selection
- Space Planning
- Design Aesthetic
- Cost Estimation
- Timeline Planning
- Professional Consultation
By carefully addressing these aspects, you can create a well-rounded plan that meets your specific needs and ensures a smooth and successful second floor addition project.
Structural Integrity
Structural integrity is of paramount importance in Second Floor Addition Plans. The existing structure must be able to withstand the additional weight of the new floor, and the new construction must be designed to meet building codes and ensure the safety of the occupants.**Assessing the Existing Structure:**Before adding a second floor, it is crucial to assess the structural integrity of the existing building. This involves evaluating the foundation, load-bearing walls, and framing to determine if they can support the additional weight. An engineer can perform a structural analysis to calculate the load capacity and identify any areas that may need reinforcement.**Reinforcements and Modifications:**In some cases, the existing structure may need to be reinforced or modified to accommodate the new floor. This may involve adding additional support beams, strengthening load-bearing walls, or upgrading the foundation. These reinforcements ensure that the building can safely handle the increased loads and maintain its structural integrity.**New Construction:**The design of the new floor must also consider structural integrity. The framing, joists, and other structural components must be sized appropriately to support the intended use of the space. Proper connections between the new and existing structures are crucial to ensure stability and prevent structural issues in the future.**Building Codes and Permits:**All Second Floor Addition Plans must comply with local building codes and zoning regulations. These codes specify minimum structural requirements to ensure the safety of buildings. Obtaining the necessary permits and inspections is essential to ensure that the addition is constructed according to code and meets the required safety standards.By carefully considering structural integrity in Second Floor Addition Plans, homeowners can ensure the safety and longevity of their renovated homes. A well-engineered and constructed second floor addition will provide a safe and enjoyable living space for years to come.
Zoning Compliance
Zoning compliance is another crucial aspect of Second Floor Addition Plans. Zoning laws regulate the use of land and buildings within specific geographic areas. These laws are established by local municipalities to ensure orderly development and maintain the character of neighborhoods.
- Height Restrictions: Zoning laws often impose height restrictions on buildings, limiting the number of stories that can be built. Homeowners planning a second floor addition must ensure that the new construction complies with the height limits for their property.
- Setback Requirements: Setback requirements specify the minimum distance that a building must be set back from property lines. These requirements help to maintain adequate space between buildings and ensure proper access for emergency vehicles and utilities.
- Lot Coverage: Zoning laws may also limit the amount of land that can be covered by buildings. This is known as lot coverage. When planning a second floor addition, homeowners must consider the existing lot coverage and ensure that the new construction does not exceed the allowable percentage.
- Permits and Approvals: Before starting any construction, it is essential to obtain the necessary permits and approvals from the local zoning board. Submitting Second Floor Addition Plans for review and approval ensures that the project complies with zoning regulations and meets the required standards.
By carefully considering zoning compliance in Second Floor Addition Plans, homeowners can avoid potential conflicts with local authorities and ensure that their project is approved and constructed according to regulations. A well-planned and compliant addition will contribute to the overall harmony and aesthetic appeal of the neighborhood.
Building Codes
Building codes are a set of regulations established by local authorities to ensure the safety and structural integrity of buildings. Second Floor Addition Plans must adhere to these codes to guarantee the stability, durability, and habitability of the new construction.
- Structural Requirements: Building codes specify minimum structural requirements for second floor additions, including the size and spacing of framing members, the strength of load-bearing walls, and the design of connections between the new and existing structures. These requirements are crucial to ensure that the addition can safely support the intended loads and resist potential hazards such as earthquakes and high winds.
- Fire Safety: Building codes also include provisions for fire safety in second floor additions. These provisions may include requirements for fire-resistant materials, smoke detectors, and fire sprinklers. Proper fire safety measures help to minimize the risk of fire and protect the occupants in case of an emergency.
- Energy Efficiency: Building codes often incorporate energy efficiency standards to reduce energy consumption and promote sustainability. These standards may include requirements for insulation, energy-efficient windows and appliances, and renewable energy systems. By meeting energy efficiency standards, homeowners can reduce their energy bills and contribute to environmental protection.
- Accessibility: Building codes may also include accessibility requirements for second floor additions. These requirements aim to ensure that the addition is accessible to individuals with disabilities. This may include the provision of ramps, elevators, or other assistive devices to facilitate access to all levels of the home.
By complying with building codes in Second Floor Addition Plans, homeowners can ensure that their new construction is safe, durable, energy-efficient, and accessible. Adhering to these codes not only protects the occupants but also contributes to the overall quality and value of the home.
Material Selection
Choosing the right materials for a second floor addition is crucial for ensuring durability, structural integrity, and aesthetic appeal. Several factors should be considered when selecting materials, including:
- Structural Requirements: The materials used for framing, joists, and other structural components must meet the structural requirements specified in the Second Floor Addition Plans. These requirements are based on factors such as the span of the floor, the weight it will bear, and the local building codes.
- Durability: The materials used for the exterior cladding, roofing, and windows should be durable and resistant to weathering. This is especially important in areas with harsh climates or exposure to moisture. Durable materials will help to protect the addition from damage and ensure its longevity.
- Energy Efficiency: Energy-efficient materials can help to reduce energy consumption and lower utility bills. This may include insulation, energy-efficient windows, and roofing materials that reflect sunlight and reduce heat gain.
- Cost: The cost of materials is a significant factor to consider when planning a second floor addition. Homeowners should research different material options and compare their costs to find the best balance between quality and affordability.
Commonly used materials for second floor additions include:
- Framing: Wood, steel, and engineered lumber are commonly used for framing second floor additions. Each material has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of strength, durability, and cost.
- Exterior Cladding: Vinyl siding, fiber cement siding, and brick are popular choices for exterior cladding. These materials offer a range of styles, colors, and textures to complement the existing home.
- Roofing: Asphalt shingles, metal roofing, and tile roofing are common roofing materials for second floor additions. The choice of roofing material depends on factors such as durability, cost, and aesthetic preferences.
- Windows: Energy-efficient windows with double or triple glazing can help to reduce heat loss and improve indoor comfort. Vinyl, wood, and aluminum are common frame materials for windows.
Space Planning
Space planning is a crucial aspect of Second Floor Addition Plans, as it determines the layout and functionality of the new space. Careful planning is necessary to create a cohesive and efficient living environment that meets the specific needs of the occupants.
- Defining Functional Zones:
The first step in space planning is to define the different functional zones within the second floor addition. This may include bedrooms, bathrooms, a home office, or a family room. Each zone should be designed to accommodate its intended use and provide a comfortable and functional space. - Maximizing Natural Light:
Natural light can significantly enhance the ambiance and livability of the new space. When planning the layout, consider the placement of windows and skylights to maximize natural light penetration. This can help to reduce energy consumption and create a more inviting and cheerful atmosphere. - Creating Flow and Circulation:
The layout of the second floor addition should promote smooth flow and circulation between different areas. Avoid creating dead-end spaces or awkward transitions. Wide hallways, open floor plans, and well-placed doorways can facilitate easy movement throughout the space. - Optimizing Storage:
Storage is an important consideration in any home addition. Incorporate ample storage solutions into the design, such as built-in closets, drawers, and shelves. This will help to keep the space organized and clutter-free, maximizing its functionality and livability.
By carefully considering space planning in Second Floor Addition Plans, homeowners can create a functional and inviting living space that meets their specific needs and enhances their quality of life.
Design Aesthetic
The design aesthetic of a second floor addition should complement the existing home while also creating a cohesive and visually appealing living space. Several factors contribute to the overall design aesthetic, including:
- Architectural Style:
The architectural style of the second floor addition should harmonize with the existing home. This may involve matching the roofline, exterior materials, and overall form. However, it is also possible to create a contrasting addition that adds a modern or contemporary touch to a traditional home.
(continue up to 4 point)
Cost Estimation
Cost estimation is a crucial aspect of Second Floor Addition Plans, as it helps homeowners budget for the project and make informed decisions. Several factors influence the cost of a second floor addition, including:
- Size:
The size of the addition is a major factor in determining its cost. Larger additions require more materials, labor, and time to complete, which can increase the overall expense.
- Complexity:
The complexity of the addition’s design and construction can also affect the cost. Additions with intricate architectural features, multiple levels, or specialized materials will typically be more expensive than simpler designs.
- Materials:
The choice of materials used for framing, exterior cladding, roofing, and windows can significantly impact the cost of the addition. Higher quality and more durable materials will generally cost more than basic materials.
- Labor:
The cost of labor is another major factor to consider. The cost of labor will vary depending on the location, the availability of skilled workers, and the complexity of the project.
In addition to these factors, homeowners should also consider the cost of permits, inspections, and site preparation. These costs can vary depending on local regulations and the specific requirements of the project.
Timeline Planning
Timeline planning is crucial for Second Floor Addition Plans, as it helps homeowners manage the project’s schedule, coordinate contractors, and avoid costly delays. Several factors should be considered when creating a realistic timeline, including:
- Design and Permitting:
The design and permitting phase can take several weeks or months, depending on the complexity of the addition and local building regulations. Homeowners should factor in time for architectural drawings, engineering calculations, and permit applications.
- Material Procurement:
Ordering and delivering materials can also take time, especially if specialized or custom materials are required. Homeowners should work with their contractor to determine lead times for materials and schedule deliveries accordingly.
- Construction Schedule:
The construction schedule is the most critical part of the timeline. Homeowners should work with their contractor to develop a detailed schedule that outlines the sequence of construction activities, including framing, roofing, siding, and interior finishing. Realistic timeframes should be established for each task, considering weather conditions and potential delays.
- Inspections and Approvals:
Building inspections are required at various stages of construction to ensure compliance with building codes and safety standards. Homeowners should schedule inspections in advance and allow time for any necessary corrections or modifications.
By carefully considering timeline planning in Second Floor Addition Plans, homeowners can avoid costly delays and ensure that their project is completed on time and within budget.
Professional Consultation
Seeking professional consultation is highly recommended when planning a second floor addition. Architects, engineers, and contractors can provide valuable expertise, ensuring the safety, functionality, and aesthetic appeal of the project.
- Architectural Design:
An architect can create detailed Second Floor Addition Plans that meet the specific requirements of the homeowners and comply with building codes. They can design a cohesive addition that complements the existing home’s architectural style and maximizes space utilization.
- Structural Engineering:
A structural engineer can assess the existing structure and design the addition’s framing and foundation to ensure its structural integrity. They can determine the appropriate materials and construction methods to support the added weight and meet safety standards.
- Contractor Selection:
A contractor can assist in selecting qualified subcontractors and overseeing the construction process. They can provide recommendations, negotiate contracts, and ensure that the project is completed according to the plans and specifications.
- Permitting and Inspections:
A contractor can help obtain the necessary building permits and arrange for inspections throughout the construction process. They are familiar with local building codes and can ensure that the addition complies with all requirements.
By consulting with professionals, homeowners can gain peace of mind knowing that their Second Floor Addition Plans are well-conceived, structurally sound, and executed to the highest standards. Professional consultation can ultimately save time, money, and potential headaches during the construction process.










Related Posts