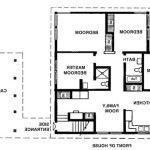
Tudor floor plans are blueprints or diagrams that depict the layout and arrangement of rooms and spaces within a Tudor-style building. Tudor architecture, prevalent in England during the Tudor period (1485-1603), is characterized by its distinctive features such as steeply pitched roofs, half-timbered walls, and elaborate chimneys.
Tudor floor plans serve as valuable tools for architects, historians, and property owners seeking to understand or restore Tudor-era structures. They provide insights into the daily life, social hierarchy, and architectural innovations of the Tudor period. For instance, the Haddon Hall in Derbyshire, England, showcases a complex Tudor floor plan, featuring grand halls, private chambers, and service areas, reflecting the elaborate lifestyle of the Vernon family who resided there.
In the following sections, we will delve into the key characteristics of Tudor floor plans, exploring their evolution, room arrangements, and the influence they had on the development of domestic architecture in England.
Tudor floor plans are characterized by distinct features that reflect the architectural style and social customs of the Tudor period.
- Central great hall
- Private chambers
- Service areas
- Steeply pitched roofs
- Half-timbered walls
- Elaborate chimneys
- Bay windows
- Spiral staircases
- Galleries
- Courtyards
These elements combined to create functional and aesthetically pleasing living spaces that catered to the needs of Tudor society.
Central great hall
The central great hall was the heart of a Tudor home. It was a large, open space that served as the main living area for the family and their guests.
- Multi-purpose space: The great hall was used for a variety of activities, including dining, entertaining, and sleeping. It was also the place where the family would gather to hear news and stories from the outside world.
- Social hierarchy: The arrangement of the great hall reflected the social hierarchy of the Tudor period. The lord and lady of the house would sit at the high table, which was placed on a raised platform at one end of the hall. The rest of the family and guests would sit at lower tables, according to their rank.
- Symbol of status: The size and grandeur of the great hall was a symbol of the wealth and status of the family. The most impressive great halls were found in the homes of the nobility and gentry.
- Architectural innovation: The Tudor period saw the development of new architectural techniques that allowed for the construction of larger and more elaborate great halls. These techniques included the use of hammerbeam roofs and bay windows.
The central great hall was an essential part of Tudor life. It was a space that brought the family together and reflected the social and architectural values of the period.
Private chambers
In addition to the central great hall, Tudor homes also included a number of private chambers. These chambers were used for sleeping, dressing, and other private activities.
The most important private chamber was the solar. The solar was the private apartment of the lord and lady of the house. It was typically located on the upper floor of the house and consisted of a bedroom, a dressing room, and a privy.
Other private chambers included the withdrawing chamber, the guest chamber, and the children’s chambers. The withdrawing chamber was a private sitting room where the family could retreat to after dinner. The guest chamber was used to accommodate guests who were staying overnight. The children’s chambers were typically located on the upper floors of the house.
Private chambers were often decorated with tapestries, paintings, and other fine furnishings. The walls were often hung with tapestries, which were used to insulate the rooms and to add color and decoration. The floors were typically covered with rushes or carpets.
Private chambers were an important part of Tudor homes. They provided the family with a space to retreat to for privacy and relaxation.
Service areas
In addition to the central great hall and private chambers, Tudor homes also included a number of service areas. These areas were used for cooking, cleaning, and other household tasks.
- Kitchen: The kitchen was the heart of the Tudor household. It was typically located in a separate building from the main house, to reduce the risk of fire. The kitchen was equipped with a large fireplace for cooking and heating. It also had a number of other features, such as a bread oven, a sink, and a dresser.
- Buttery: The buttery was a small room where food and drink were stored. It was typically located near the kitchen and was used to keep food cool and fresh.
- Pantry: The pantry was a larger room where food was stored for longer periods of time. It was typically located in a cool, dry place.
- Laundry: The laundry was a room where clothes were washed and dried. It was typically located in a separate building from the main house, to reduce the risk of fire.
Service areas were an essential part of Tudor homes. They provided the family with the space and facilities they needed to cook, clean, and perform other household tasks.
Steeply pitched roofs
Steeply pitched roofs are one of the most distinctive features of Tudor architecture. They are typically constructed with a slope of 45 degrees or more, and are often covered with tiles or slates. The steep pitch of the roof helps to shed water and snow quickly and efficiently, which is important in the often rainy and snowy climate of England.The steep pitch of the roof also creates a large attic space, which can be used for storage or as living space. In some cases, the attic space was even used as a separate apartment, known as a garret. Garrets were often used by servants or poor tenants.The steeply pitched roof is also a visually striking feature, and it helps to give Tudor buildings their distinctive character. The roofs are often decorated with chimneys, gables, and other architectural details, which add to their visual appeal.
The steeply pitched roof is an essential part of the Tudor floor plan. It provides protection from the elements, creates additional living space, and adds to the visual appeal of the building.
Half-timbered walls
Half-timbered walls are a defining feature of Tudor architecture. They are constructed with a framework of wooden beams, which are then filled in with a mixture of plaster and wattle. The beams are typically exposed on the exterior of the building, giving it a distinctive black-and-white appearance.
- Structural support: The half-timbered framework provides structural support for the building. The beams are carefully joined together to create a strong and durable structure that can withstand the weight of the roof and walls.
- Insulation: The plaster and wattle infill between the beams provides insulation for the building. This helps to keep the building warm in the winter and cool in the summer.
- Ventilation: The gaps between the beams allow for ventilation, which helps to prevent damp and rot.
- Aesthetic appeal: Half-timbered walls are also visually appealing. The exposed beams and the contrast between the black beams and the white plaster create a distinctive and charming appearance.
Half-timbered walls are an essential part of the Tudor floor plan. They provide structural support, insulation, ventilation, and aesthetic appeal.
Elaborate chimneys
Elaborate chimneys are another distinctive feature of Tudor architecture. They are typically constructed of brick or stone, and are often decorated with intricate carvings and moldings. The chimneys are often very tall and slender, and they often have multiple flues to accommodate the different fireplaces in the house.The elaborate chimneys of Tudor homes served a number of purposes. First, they provided a means of venting smoke and fumes from the fireplaces. Second, they helped to draw air into the fireplaces, which helped to keep the fires burning. Third, the chimneys helped to support the roof structure of the house.In addition to their functional purposes, the elaborate chimneys of Tudor homes were also a status symbol. The height and grandeur of a chimney reflected the wealth and status of the family who lived in the house. The most elaborate chimneys were found on the homes of the nobility and gentry.The elaborate chimneys of Tudor homes are a testament to the skill and craftsmanship of the Tudor builders. They are a beautiful and functional feature of Tudor architecture, and they continue to be admired today.
The elaborate chimneys of Tudor homes are an essential part of the Tudor floor plan. They provide a means of venting smoke and fumes, drawing air into the fireplaces, supporting the roof structure, and reflecting the wealth and status of the family who lived in the house.
Bay windows
Bay windows are another distinctive feature of Tudor architecture. They are typically constructed with a series of windows that project outward from the wall of the building, creating a small alcove. Bay windows are often found in the great hall of a Tudor home, where they provide a view of the surrounding landscape.
- Increased light: Bay windows allow for more natural light to enter the room, which makes the space feel larger and brighter. This is especially important in the great hall, which was often the main living space for the family.
- Improved ventilation: Bay windows also help to improve ventilation in the room. When the windows are open, they allow air to circulate more easily, which helps to keep the space fresh and comfortable.
- Extended seating: The alcove created by the bay windows can be used for additional seating. This is especially useful in the great hall, where the family and their guests would often gather for meals and entertainment.
- Aesthetic appeal: Bay windows are also a visually appealing feature. The projecting windows and the small alcove they create add depth and interest to the exterior of the building.
Bay windows are an essential part of the Tudor floor plan. They provide increased light, improved ventilation, extended seating, and aesthetic appeal.
Spiral staircases
Spiral staircases are another distinctive feature of Tudor architecture. They are typically constructed of wood or stone, and they wind their way up through the different floors of the building. Spiral staircases are often found in the great hall of a Tudor home, where they provide access to the upper floors.Spiral staircases are a space-efficient way to connect different floors of a building. They are also a visually striking feature, and they can add a touch of elegance to any home. The spiral staircases in Tudor homes are often decorated with intricate carvings and moldings, which add to their beauty.Spiral staircases can be dangerous, especially for young children and the elderly. The steps are often steep and narrow, and the lack of a handrail can make it difficult to maintain balance. However, the beauty and space-saving benefits of spiral staircases make them a popular choice for Tudor homes.Spiral staircases are an essential part of the Tudor floor plan. They provide a space-efficient and visually appealing way to connect different floors of the building. However, it is important to be aware of the potential dangers of spiral staircases, especially for young children and the elderly.
Spiral staircases are a unique and beautiful feature of Tudor architecture. They add a touch of elegance to any home, and they can also be a space-saving solution. However, it is important to be aware of the potential dangers of spiral staircases, especially for young children and the elderly.
Galleries
Galleries are another distinctive feature of Tudor architecture. They are typically long, narrow rooms that are located on the upper floors of the building. Galleries are often used as living spaces, but they can also be used for storage or as a way to connect different parts of the building.
- Increased living space: Galleries provide additional living space, which is especially important in large Tudor homes. They can be used as sitting rooms, libraries, or even bedrooms.
- Improved ventilation: Galleries are often located on the upper floors of the building, which means that they have good ventilation. This makes them a comfortable place to live, even in the hot summer months.
- Access to different parts of the building: Galleries can be used to connect different parts of the building. This makes it easy to move around the house, even if the rooms are located on different floors.
- Aesthetic appeal: Galleries are also a visually appealing feature. The long, narrow shape of the room creates a sense of depth and perspective. Galleries are often decorated with tapestries, paintings, and other works of art, which adds to their beauty.
Galleries are an essential part of the Tudor floor plan. They provide increased living space, improved ventilation, access to different parts of the building, and aesthetic appeal.
Courtyards
Courtyards are another distinctive feature of Tudor architecture. They are typically open spaces that are surrounded by the building on all sides. Courtyards are often used for outdoor living, gardening, or as a way to bring light and ventilation into the building.
- Outdoor living: Courtyards provide a space for outdoor living, even in the heart of a city. They can be used for dining, entertaining, or simply relaxing in the fresh air.
- Gardening: Courtyards are also a great place to grow plants and flowers. The sheltered environment of the courtyard protects plants from the elements, and the sunlight and warmth of the courtyard help them to thrive.
- Light and ventilation: Courtyards can be used to bring light and ventilation into the building. The open space of the courtyard allows sunlight to penetrate deep into the building, and the air can circulate freely, which helps to keep the building cool and fresh.
- Aesthetic appeal: Courtyards are also a visually appealing feature. The open space and the greenery of the plants create a sense of peace and tranquility. Courtyards are often decorated with fountains, sculptures, and other works of art, which adds to their beauty.
Courtyards are an essential part of the Tudor floor plan. They provide a space for outdoor living, gardening, light and ventilation, and aesthetic appeal.









Related Posts