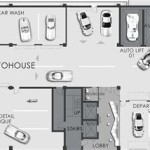
A warehouse floor plan is a critical component in optimizing warehouse operations and efficiency. It serves as a blueprint for the physical layout of the warehouse, including the arrangement of storage areas, aisles, equipment, and other facilities. By carefully designing the floor plan, businesses can maximize storage capacity, facilitate efficient material flow, and minimize operational costs.
For instance, in a manufacturing facility, a well-planned warehouse floor plan ensures that raw materials are stored near the production line, finished goods are easily accessible for shipping, and equipment is strategically placed to minimize downtime. This thoughtful arrangement optimizes inventory management, reduces handling time, and streamlines the entire manufacturing process.
In the subsequent sections of this article, we will explore the key considerations, design principles, and best practices for developing effective warehouse floor plans. We will delve into the different types of storage systems, aisle configurations, material handling equipment, and safety regulations that impact the design process. By understanding these factors, businesses can create floor plans that meet their specific operational needs and drive productivity, efficiency, and profitability.
When designing a warehouse floor plan, there are several important points to consider:
- Storage capacity
- Material flow
- Aisle configuration
- Equipment selection
- Safety regulations
- Flexibility and scalability
- Cost optimization
- Inventory management
- Receiving and shipping
- Employee efficiency
By carefully considering these factors, businesses can create a warehouse floor plan that meets their specific operational needs and drives productivity, efficiency, and profitability.
Storage capacity
Storage capacity is a critical consideration in warehouse floor plan design. It determines the amount of inventory that can be stored in the warehouse and the efficiency with which it can be accessed and retrieved. Several factors impact storage capacity, including:
- Warehouse size and shape: The overall size and shape of the warehouse will dictate the maximum amount of storage space that is available. Warehouses with high ceilings and clear spans can accommodate more storage than those with low ceilings and obstructed spaces.
- Storage system design: The type of storage system used will also impact storage capacity. Pallet racks, for example, can store more inventory than shelves or bins, but they also require more space. High-density storage systems, such as automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), can maximize storage capacity in a limited space.
- Inventory characteristics: The size, shape, and weight of the inventory will also affect storage capacity. Bulky or heavy items will require more space and may need to be stored on specialized racks or platforms.
- Aisle configuration: The width and layout of the aisles in the warehouse will impact storage capacity. Narrower aisles can accommodate more storage racks, but they can also make it more difficult to maneuver equipment and retrieve inventory.
By carefully considering these factors, businesses can design a warehouse floor plan that optimizes storage capacity while also ensuring efficient material flow and operational efficiency.
Material flow
Material flow refers to the movement of inventory and other materials through the warehouse. It encompasses all activities related to receiving, storing, picking, packing, and shipping. Efficient material flow is essential for maximizing productivity, minimizing costs, and meeting customer demand. Several factors impact material flow in a warehouse, including:
Warehouse layout
The layout of the warehouse will have a significant impact on material flow. A well-designed layout will minimize travel distances for workers and equipment, reduce congestion, and facilitate efficient inventory movement. Factors to consider when designing the warehouse layout include:
- Receiving and shipping areas: These areas should be located near each other to minimize the distance that inventory needs to be moved.
- Storage areas: Storage areas should be organized to minimize travel distances and maximize storage capacity. Similar items should be stored together, and high-turnover items should be placed in easily accessible locations.
- Picking and packing areas: These areas should be located near the shipping area to minimize the distance that orders need to be transported. Picking and packing should be organized to minimize travel distances and maximize efficiency.
- Aisle configuration: The width and layout of the aisles in the warehouse will impact material flow. Narrower aisles can accommodate more storage racks, but they can also make it more difficult to maneuver equipment and retrieve inventory.
By carefully considering these factors, businesses can design a warehouse layout that optimizes material flow and operational efficiency.
Aisle configuration
Aisle configuration is a critical factor in warehouse floor plan design. It impacts storage capacity, material flow, and operational efficiency. There are several different aisle configurations to choose from, and the best option for a particular warehouse will depend on the specific needs of the operation.
The most common aisle configuration is the grid pattern, which consists of parallel aisles that run the length of the warehouse. This configuration is simple to implement and provides good access to all storage locations. However, it can be less efficient than other configurations for warehouses with high-turnover inventory or a large number of SKUs.
Another common aisle configuration is the racetrack pattern, which consists of a single aisle that loops around the perimeter of the warehouse. This configuration is more efficient than the grid pattern for warehouses with high-turnover inventory because it minimizes travel distances for order pickers. However, it can be more difficult to implement and can require more space than the grid pattern.
Other aisle configurations include the herringbone pattern, which consists of aisles that are arranged in a V-shape, and the random pattern, which consists of aisles that are arranged in a random order. These configurations can be more efficient than the grid and racetrack patterns for warehouses with a large number of SKUs or a high volume of orders. However, they can also be more difficult to implement and can require more space.
When choosing an aisle configuration, it is important to consider the following factors:
- Storage capacity: The aisle configuration will impact the amount of storage capacity that is available in the warehouse.
- Material flow: The aisle configuration will impact the efficiency of material flow through the warehouse.
- Operational efficiency: The aisle configuration will impact the overall operational efficiency of the warehouse.
- Cost: The aisle configuration will impact the cost of implementing and maintaining the warehouse.
By carefully considering these factors, businesses can choose an aisle configuration that meets their specific operational needs and drives productivity, efficiency, and profitability.
Equipment selection
Equipment selection is a critical aspect of warehouse floor plan design. The right equipment can help to improve productivity, efficiency, and safety in the warehouse. When selecting equipment, it is important to consider the following factors:
- Type of inventory: The type of inventory that is stored in the warehouse will impact the type of equipment that is needed. For example, a warehouse that stores heavy items will need different equipment than a warehouse that stores lightweight items.
- Volume of inventory: The volume of inventory that is stored in the warehouse will also impact the type of equipment that is needed. A warehouse with a high volume of inventory will need more equipment than a warehouse with a low volume of inventory.
- Storage system: The storage system that is used in the warehouse will also impact the type of equipment that is needed. For example, a warehouse that uses pallet racks will need different equipment than a warehouse that uses shelves or bins.
- Aisle configuration: The aisle configuration in the warehouse will also impact the type of equipment that is needed. For example, a warehouse with narrow aisles will need different equipment than a warehouse with wide aisles.
Some of the most common types of equipment used in warehouses include:
- Forklifts: Forklifts are used to move pallets and other heavy items around the warehouse.
- Order pickers: Order pickers are used to retrieve individual items from storage racks.
- Conveyor systems: Conveyor systems are used to move items from one area of the warehouse to another.
- Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS): AS/RS are used to store and retrieve items from high-density storage racks.
By carefully considering the factors discussed above, businesses can select the right equipment for their warehouse and optimize productivity, efficiency, and safety.
Safety regulations
Safety regulations are an essential consideration in warehouse floor plan design. A well-designed floor plan will minimize the risk of accidents and injuries to workers and visitors. Some of the most important safety regulations to consider include:
Fire safety: Fire safety regulations are designed to prevent and minimize the spread of fires in warehouses. These regulations typically require warehouses to have fire sprinklers, fire alarms, and fire extinguishers. Warehouses must also have clearly marked fire exits and emergency evacuation plans.
Electrical safety: Electrical safety regulations are designed to prevent electrical fires and shocks. These regulations typically require warehouses to have properly installed and maintained electrical wiring, outlets, and lighting. Warehouses must also have ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) installed in all areas where there is a risk of electrical shock.
Material handling safety: Material handling safety regulations are designed to prevent injuries to workers who are handling materials in the warehouse. These regulations typically require warehouses to have proper lifting equipment, such as forklifts and pallet jacks. Warehouses must also have clear and concise procedures for lifting and moving materials.
Fall protection: Fall protection regulations are designed to prevent workers from falling from elevated surfaces in the warehouse. These regulations typically require warehouses to have guardrails, toe boards, and safety nets installed on all elevated surfaces. Warehouses must also have proper ladders and stairways for accessing elevated surfaces.
By carefully considering these safety regulations, businesses can design a warehouse floor plan that minimizes the risk of accidents and injuries and ensures a safe working environment for all.
Flexibility and scalability
Flexibility and scalability are important considerations in warehouse floor plan design. A flexible floor plan can be easily adapted to changes in inventory levels, product mix, and operational requirements. A scalable floor plan can be expanded or contracted to meet changing business needs. By designing a flexible and scalable floor plan, businesses can ensure that their warehouse can meet the demands of their business now and in the future.
- Adaptability to changing inventory levels: Inventory levels can fluctuate significantly over time. A flexible floor plan can be easily adapted to accommodate changes in inventory levels without disrupting operations. For example, a warehouse may need to add or remove storage racks to accommodate seasonal changes in inventory levels.
- Accommodation of different product mixes: The product mix in a warehouse can also change over time. A flexible floor plan can be easily adapted to accommodate different product mixes without disrupting operations. For example, a warehouse may need to add or remove different types of storage racks to accommodate changes in the product mix.
- Response to changes in operational requirements: Operational requirements can also change over time. A flexible floor plan can be easily adapted to meet changes in operational requirements without disrupting operations. For example, a warehouse may need to add or remove workstations to accommodate changes in the number of employees or the types of tasks being performed.
- Expansion or contraction to meet changing business needs: A scalable floor plan can be expanded or contracted to meet changing business needs. For example, a warehouse may need to be expanded to accommodate growth in sales or contracted to accommodate a decline in sales.
By carefully considering flexibility and scalability, businesses can design a warehouse floor plan that can meet the demands of their business now and in the future.
Cost optimization
Cost optimization is an important consideration in warehouse floor plan design. A well-designed floor plan can help to reduce operating costs and improve profitability. Here are some of the key cost optimization considerations for warehouse floor plan design:
- Space utilization: The warehouse floor plan should be designed to maximize space utilization and minimize wasted space. This can be achieved by using high-density storage systems, such as pallet racks and automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS). It is also important to consider the flow of materials through the warehouse and to design the floor plan to minimize travel distances and congestion.
- Material handling equipment: The type of material handling equipment used in the warehouse can also impact costs. For example, forklifts are more expensive to purchase and operate than pallet jacks. However, forklifts can be more efficient in warehouses with high ceilings and narrow aisles. It is important to carefully consider the type of material handling equipment that is needed for the specific warehouse operation.
- Labor costs: The warehouse floor plan should be designed to minimize labor costs. This can be achieved by using automated systems, such as AS/RS, and by designing the floor plan to minimize travel distances and congestion. It is also important to consider the number of employees that are needed to operate the warehouse and to design the floor plan to minimize the need for overtime and additional staff.
- Energy costs: The warehouse floor plan can also impact energy costs. For example, warehouses with high ceilings and good natural lighting can reduce the need for artificial lighting. It is also important to consider the type of heating and cooling systems that are used in the warehouse and to design the floor plan to minimize energy consumption.
By carefully considering these cost optimization factors, businesses can design a warehouse floor plan that minimizes operating costs and improves profitability.
Inventory management
Inventory management is a critical aspect of warehouse operations. The warehouse floor plan can have a significant impact on inventory management efficiency. A well-designed floor plan can help to improve inventory accuracy, reduce inventory shrinkage, and optimize inventory turnover.
One of the most important aspects of inventory management is inventory accuracy. Inventory accuracy refers to the degree to which the warehouse’s records match the actual inventory on hand. Inaccurate inventory records can lead to a number of problems, including lost sales, overstocking, and stockouts. A well-designed warehouse floor plan can help to improve inventory accuracy by minimizing the risk of errors. For example, a floor plan that uses clear and concise labeling and signage can help to reduce the risk of picking errors. Additionally, a floor plan that minimizes travel distances and congestion can help to reduce the risk of inventory damage and loss.
Another important aspect of inventory management is inventory shrinkage. Inventory shrinkage refers to the loss of inventory due to theft, damage, or other factors. A well-designed warehouse floor plan can help to reduce inventory shrinkage by creating a secure and organized environment. For example, a floor plan that uses security cameras and access control systems can help to deter theft. Additionally, a floor plan that uses proper lighting and ventilation can help to prevent inventory damage.
Finally, a well-designed warehouse floor plan can help to optimize inventory turnover. Inventory turnover refers to the number of times that inventory is sold and replaced over a period of time. A high inventory turnover rate indicates that the warehouse is efficiently managing its inventory. A well-designed floor plan can help to optimize inventory turnover by minimizing travel distances and congestion. Additionally, a floor plan that uses automated systems, such as AS/RS, can help to improve inventory accuracy and reduce inventory shrinkage.
By carefully considering inventory management requirements, businesses can design a warehouse floor plan that improves inventory accuracy, reduces inventory shrinkage, and optimizes inventory turnover.
Receiving and shipping
The receiving and shipping areas are critical components of a warehouse floor plan. These areas are responsible for the efficient flow of goods into and out of the warehouse. A well-designed receiving and shipping area can help to reduce costs, improve customer service, and increase productivity.
- Location: The receiving and shipping areas should be located near each other to minimize the distance that goods need to be moved. They should also be located near the loading docks to facilitate the loading and unloading of goods.
- Size: The receiving and shipping areas should be large enough to accommodate the volume of goods that are being received and shipped. They should also be able to accommodate the necessary equipment, such as forklifts and pallet jacks.
- Layout: The receiving and shipping areas should be laid out in a way that minimizes congestion and improves efficiency. The receiving area should be designed to allow for the quick and easy unloading of goods. The shipping area should be designed to allow for the efficient loading of goods onto trucks or other vehicles.
- Equipment: The receiving and shipping areas should be equipped with the necessary equipment to handle the goods that are being received and shipped. This equipment may include forklifts, pallet jacks, conveyors, and scales.
By carefully considering these factors, businesses can design a receiving and shipping area that meets their specific needs and improves the overall efficiency of their warehouse operation.
Employee efficiency
The warehouse floor plan can have a significant impact on employee efficiency. A well-designed floor plan can help to reduce employee fatigue, improve productivity, and increase safety. Here are some of the key employee efficiency considerations for warehouse floor plan design:
Minimizing travel distances: Employees should not have to walk or travel long distances to perform their tasks. The warehouse floor plan should be designed to minimize travel distances between different areas of the warehouse, such as the receiving area, the storage area, and the shipping area. This can be achieved by using a grid-based layout or a U-shaped layout.
Reducing congestion: Congestion can slow down employees and make it difficult to perform their tasks safely. The warehouse floor plan should be designed to minimize congestion by providing wide aisles and clear pathways. This can be achieved by using a grid-based layout or a racetrack layout.
Improving ergonomics: The warehouse floor plan should be designed to promote good ergonomics and reduce the risk of employee injuries. This can be achieved by providing adjustable workstations, using proper lifting equipment, and providing adequate lighting.
Creating a safe environment: The warehouse floor plan should be designed to create a safe environment for employees. This can be achieved by providing proper lighting, installing safety features such as guardrails and safety mats, and implementing a regular maintenance program.
By carefully considering these employee efficiency factors, businesses can design a warehouse floor plan that improves employee productivity, reduces fatigue, and enhances safety.










Related Posts