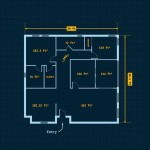
Yurt floor plans refer to the layout and organization of the interior space within a yurt, a traditional portable dwelling used by nomadic communities in Central Asia. Floor plans determine the functional and aesthetic aspects of the yurt, defining the arrangement of living areas, storage spaces, and central hearth.
Yurt floor plans often adhere to specific cultural and regional traditions, with variations in design depending on the purpose and size of the yurt. For instance, some yurt floor plans incorporate a central hearth surrounded by sleeping and living areas, while others may feature multiple partitioned spaces for privacy or ceremonial purposes.
In the following sections, we will delve into the various aspects of yurt floor plans, exploring their historical significance, structural considerations, and contemporary adaptations for modern living.
When considering yurt floor plans, there are several important points to keep in mind:
- Central Hearth: Focal point for cooking, heating, and gathering.
- Sleeping Quarters: Designated areas for beds and sleeping arrangements.
- Living Space: Open and flexible area for daily activities.
- Storage Spaces: Shelves, chests, and nooks for storing belongings.
- Partitions: Optional dividers to create separate spaces for privacy or specific purposes.
- Orientation: Positioning of the door and windows for optimal light and ventilation.
- Structural Support: Reinforcement elements to ensure stability and durability.
- Cultural Influences: Regional variations in floor plans based on cultural traditions.
- Modern Adaptations: Modifications to suit contemporary living needs, such as incorporating electricity and insulation.
By considering these factors, yurt floor plans can be tailored to meet specific requirements and preferences, creating functional and comfortable living spaces within the unique environment of a yurt.
Central Hearth: Focal point for cooking, heating, and gathering.
The central hearth is a defining feature of yurt floor plans, serving as the heart of the dwelling and a focal point for daily life. It is typically located in the center of the yurt, directly beneath the smoke hole in the roof. The hearth provides a source of heat for cooking and warmth, and it also serves as a gathering place for family and friends.
The central hearth is often constructed using a raised platform or fire pit, which helps to contain the fire and protect the yurt from sparks. The platform or fire pit is usually made of stone, mud, or other fire-resistant materials. Around the hearth, there is often a designated area for cooking, with shelves or hooks for storing cooking utensils and food supplies.
In addition to its practical functions, the central hearth also holds cultural and symbolic significance. It is often seen as a representation of the family and the home, and it is a place where important ceremonies and rituals are performed. In some cultures, the hearth is considered to be a sacred space, and it is treated with respect and reverence.
The central hearth remains an essential element of yurt floor plans, providing both functional and symbolic value. It is a reminder of the nomadic heritage of yurt dwellers and a testament to the importance of community and family life.
Sleeping Quarters: Designated areas for beds and sleeping arrangements.
Sleeping quarters are an important aspect of yurt floor plans, as they provide designated spaces for rest and privacy. In traditional yurt designs, sleeping areas are typically located around the perimeter of the yurt, with beds or sleeping platforms arranged against the curved walls.
- Designated sleeping areas: Sleeping quarters in yurts are often defined by specific areas designated for beds or sleeping platforms. These areas may be separated by partitions or curtains to create a sense of privacy and separation from the rest of the living space.
- Bed platforms: Bed platforms are common in yurts, as they provide a raised surface for sleeping and help to keep bedding off the cold ground. Platforms can be constructed from wood, bamboo, or other sturdy materials, and they may be covered with mattresses, blankets, or sheepskins for comfort.
- Built-in storage: Sleeping quarters in yurts may also incorporate built-in storage spaces, such as shelves or drawers, for storing bedding, clothing, and other personal belongings. This helps to keep the living space organized and clutter-free.
- Orientation: The orientation of sleeping quarters within the yurt is often carefully considered to maximize comfort and privacy. Beds may be positioned to face the central hearth for warmth and light, or they may be placed in areas that receive natural light from windows or skylights.
Sleeping quarters in yurts are designed to provide comfortable and private spaces for rest and relaxation. They reflect the nomadic lifestyle of yurt dwellers, who value flexibility and adaptability in their living arrangements.
Living Space: Open and flexible area for daily activities.
The living space in a yurt is an open and flexible area that serves as the main hub for daily activities. It is typically located in the center of the yurt, surrounding the central hearth. The living space is used for a variety of purposes, including cooking, eating, socializing, working, and playing.
The open and flexible nature of the living space allows yurt dwellers to adapt the space to their specific needs and preferences. For example, the living space can be easily rearranged to accommodate different activities, such as setting up a dining area for meals or creating a cozy seating area for relaxation.
The living space is also often used for storage. Shelves, chests, and other storage solutions can be placed around the perimeter of the living space to keep belongings organized and out of the way. This helps to maintain a sense of openness and spaciousness in the yurt.
The living space in a yurt is a versatile and functional area that provides a comfortable and inviting space for daily life. It is a reflection of the nomadic lifestyle of yurt dwellers, who value flexibility and adaptability in their living arrangements.
Storage Spaces: Shelves, chests, and nooks for storing belongings.
Storage spaces are an essential aspect of yurt floor plans, as they provide designated areas for storing belongings and keeping the living space organized. Yurts typically incorporate a variety of storage solutions, including shelves, chests, and nooks, to accommodate the needs of yurt dwellers.
- Shelves: Shelves are a common storage solution in yurts, as they provide a convenient and accessible way to store items. Shelves can be mounted on walls or suspended from the ceiling, and they can be used to store a variety of items, such as food supplies, cooking utensils, clothing, and personal belongings.
- Chests: Chests are another popular storage solution in yurts. They provide a secure and dust-free place to store valuable items or items that are not frequently used. Chests can be made from a variety of materials, such as wood, metal, or fabric, and they can be decorated to match the yurt’s interior design.
- Nooks: Nooks are small, recessed areas in the yurt’s walls that can be used for storage. Nooks are often used to store items that are not frequently used, such as extra bedding or seasonal items. Nooks can also be used to display decorative items or artwork.
- Built-in storage: Some yurts incorporate built-in storage spaces, such as drawers or cabinets, into the yurt’s design. Built-in storage spaces are a convenient and space-saving way to store belongings, and they can help to keep the yurt organized and clutter-free.
Storage spaces in yurts are designed to be functional and efficient, providing yurt dwellers with ample space to store their belongings and keep their living space organized. The use of shelves, chests, nooks, and built-in storage solutions allows yurt dwellers to adapt the yurt’s interior to their specific needs and preferences.
Partitions: Optional dividers to create separate spaces for privacy or specific purposes.
Partitions are optional dividers that can be used to create separate spaces within a yurt. They are typically made from fabric, felt, or other lightweight materials, and they can be easily moved or removed to adapt the yurt’s interior to different needs and preferences.
Partitions are often used to create private sleeping areas within the yurt. They can also be used to create separate spaces for specific purposes, such as a cooking area, a storage area, or a workspace. Partitions can also be used to create a sense of separation between the living space and the central hearth, which can be helpful for regulating temperature and airflow within the yurt.
Partitions are a versatile and flexible way to customize the interior of a yurt. They can be used to create a variety of different layouts and configurations, and they can be easily adjusted to accommodate changing needs and preferences. This makes partitions a valuable tool for yurt dwellers who want to create a comfortable and functional living space.
In addition to their practical functions, partitions can also be used to add a decorative touch to the yurt’s interior. Partitions can be made from a variety of different materials and colors, and they can be decorated with embroidery, appliqus, or other embellishments. This allows yurt dwellers to personalize their living space and create a unique and inviting atmosphere.
Partitions are an essential element of yurt floor plans, as they provide a way to create separate spaces for privacy or specific purposes. They are a versatile and flexible solution that can be adapted to meet the needs and preferences of yurt dwellers. Partitions also add a decorative touch to the yurt’s interior, making them a valuable tool for creating a comfortable and inviting living space.
Orientation: Positioning of the door and windows for optimal light and ventilation.
The orientation of the door and windows in a yurt floor plan is an important consideration for ensuring optimal light and ventilation. The position of these openings can impact the yurt’s interior temperature, airflow, and natural lighting conditions.
Sunlight and natural lighting: The positioning of windows and skylights can be carefully planned to maximize natural light and solar heat gain. Windows facing south or west will allow for more sunlight to enter the yurt during the day, providing warmth and reducing the need for artificial lighting. Skylights can also be incorporated into the roof of the yurt to provide additional natural light and a sense of openness.
Ventilation and airflow: The placement of windows and doors can also be used to promote ventilation and airflow within the yurt. Windows and doors located on opposite sides of the yurt will create a cross-breeze, which can help to regulate temperature and remove stale air. Vents or small windows near the top of the yurt can also be used to release hot air and improve ventilation.
Privacy and views: The orientation of windows and doors should also take into account privacy and views. Windows and doors facing common areas or neighboring yurts should be positioned to minimize privacy concerns. Windows facing scenic views or natural landscapes can provide a connection to the outdoors and enhance the overall ambiance of the yurt.
By carefully considering the orientation of the door and windows, yurt dwellers can create a comfortable and inviting living space that is filled with natural light and fresh air. The strategic placement of these openings can also help to reduce energy consumption and improve the overall well-being of yurt dwellers.
Structural Support: Reinforcement elements to ensure stability and durability.
The structural support of a yurt is crucial for ensuring its stability and durability in various weather conditions. Yurts incorporate several reinforcement elements to withstand strong winds, heavy snow loads, and other environmental stresses.
- Tension Band: A tension band is a strong rope or cable that runs around the circumference of the yurt, just below the roofline. It helps to distribute the weight of the roof and walls evenly, preventing the yurt from collapsing under pressure. The tension band is typically made of durable materials such as nylon or steel, and it is tightened using a windlass or other tensioning device.
- Roof Ribs: Roof ribs are curved wooden poles that form the framework of the yurt’s roof. They are attached to the crown ring at the top of the yurt and extend down to the walls. The roof ribs provide support for the roof covering and help to distribute the weight of snow and wind loads. The number and spacing of the roof ribs depend on the size and design of the yurt.
- Wall Lattice: The wall lattice is a framework of wooden poles that forms the walls of the yurt. It consists of vertical poles, horizontal poles, and diagonal braces. The wall lattice provides support for the yurt’s covering and helps to resist wind forces. The spacing and thickness of the wall lattice depend on the size and intended use of the yurt.
- Doorway Reinforcement: The doorway is a potential weak point in the yurt’s structure, as it creates an opening in the wall lattice. To reinforce the doorway, additional wooden poles or metal brackets are often used to strengthen the frame around the door. This helps to prevent the doorway from collapsing or deforming under pressure.
These structural support elements work together to create a strong and stable yurt that can withstand the rigors of nomadic life. The use of tension bands, roof ribs, wall lattice, and doorway reinforcement ensures that yurts can provide safe and durable shelter in a variety of environments.
Cultural Influences: Regional variations in floor plans based on cultural traditions.
Yurt floor plans exhibit regional variations that reflect the diverse cultural traditions of nomadic communities across Central Asia. These variations are influenced by factors such as climate, lifestyle, and social customs.
- Central Asian Yurts: Traditional Central Asian yurts are characterized by a circular floor plan with a central hearth and a domed roof. The central hearth is used for cooking, heating, and gathering, while the surrounding space is divided into designated areas for sleeping, storage, and daily activities. The yurt’s covering is typically made of felt or animal skins, providing insulation and protection from the elements.
- Mongolian Yurts: Mongolian yurts are known for their large size and elaborate decorations. They feature a spacious circular floor plan with a central hearth and a high domed roof. The yurt’s covering is often made of multiple layers of felt, providing excellent insulation against extreme temperatures. Mongolian yurts also incorporate intricate designs and patterns on the felt covering, reflecting the cultural and artistic traditions of the Mongolian people.
- Kazakh Yurts: Kazakh yurts are adapted to the harsh climate of the Kazakh steppes. They have a smaller, more compact floor plan compared to Mongolian yurts, with a central hearth and a lower roof. The yurt’s covering is typically made of felt or woven goat hair, providing insulation and protection from strong winds and cold temperatures. Kazakh yurts also feature distinctive wooden latticework on the walls, adding structural support and decorative elements.
- Kyrgyz Yurts: Kyrgyz yurts are designed for mobility and adaptability. They have a lightweight, collapsible frame and a portable felt covering. The floor plan is typically circular, with a central hearth and a surrounding space divided into functional areas. Kyrgyz yurts are often decorated with colorful felt appliqus and embroidery, reflecting the artistic traditions of the Kyrgyz people.
These cultural influences have shaped the diverse floor plans of yurts, creating unique and functional living spaces that reflect the traditions and lifestyles of nomadic communities across Central Asia.
Modern Adaptations: Modifications to suit contemporary living needs, such as incorporating electricity and insulation.
In recent years, yurts have undergone modern adaptations to meet the changing needs and lifestyles of contemporary yurt dwellers. These adaptations incorporate modern conveniences and technologies while preserving the traditional essence of yurt living.
Electrical Systems: Traditional yurts relied on natural light and fire for illumination. Modern yurts often incorporate electrical systems to provide convenient and reliable lighting, power outlets, and appliances. Electrical wiring is carefully installed within the yurt’s structure, with outlets and switches placed for easy access. Solar panels or portable generators are commonly used to provide off-grid electricity, allowing yurt dwellers to enjoy the comforts of modern living even in remote locations.
Insulation: Traditional yurts were insulated with layers of felt or animal skins, providing adequate protection from the elements. Modern yurts often incorporate additional insulation materials to enhance comfort and energy efficiency. Foam insulation, fiberglass batting, or spray foam can be installed within the yurt’s walls and roof, providing better insulation against extreme temperatures. This allows yurt dwellers to enjoy a more comfortable living environment throughout the year, reducing the need for additional heating or cooling.
Heating and Cooling Systems: Modern yurts may incorporate heating and cooling systems to provide a comfortable indoor climate. Small wood-burning stoves or electric heaters can be used to provide warmth during cold weather. Air conditioners or evaporative coolers can be used to cool the yurt during hot weather. These systems are typically powered by electricity or propane, allowing yurt dwellers to maintain a comfortable temperature inside the yurt regardless of the outdoor conditions.
Modern adaptations to yurt floor plans have enhanced the functionality and comfort of yurts, making them suitable for contemporary living needs. By incorporating electricity, insulation, and heating and cooling systems, yurt dwellers can enjoy the conveniences of modern life while embracing the unique and traditional aspects of yurt living.










Related Posts