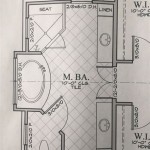
An example floor plan drawing is a detailed, scaled drawing that depicts the layout of a building or room, showing the placement of walls, doors, windows, and other features. It serves as a crucial tool for architects, builders, and interior designers, providing a comprehensive overview of the spatial relationships and dimensions within a structure.
Floor plan drawings find widespread application in various scenarios. For instance, when buying or renting a property, they assist potential occupants in visualizing the space and assessing its functionality. In commercial settings, they are essential for planning office layouts, determining traffic flow, and ensuring compliance with building codes.
Moving forward, this article will delve into the essential elements of an example floor plan drawing, exploring its components and their significance in conveying spatial information. We will discuss the different types of floor plans, their uses, and the benefits they offer in the design and construction process.
An example floor plan drawing is a valuable tool that provides a clear understanding of a building’s layout. Here are 8 important points to consider:
- Accurate dimensions: Ensures proper scale and proportions.
- Detailed fixtures: Shows placement of doors, windows, and other elements.
- Wall specifications: Indicates wall types, materials, and thickness.
- Room labels: Identifies the function of each room.
- Furniture layout: Illustrates potential furniture arrangements.
- Circulation paths: Highlights traffic flow and accessibility.
- Lighting plan: Indicates lighting fixtures and their placement.
- Compliance with codes: Adheres to building regulations and standards.
Understanding these points will enhance the effectiveness of example floor plan drawings in conveying spatial information and facilitating informed decision-making.
Accurate dimensions: Ensures proper scale and proportions.
Accurate dimensions are crucial in example floor plan drawings to ensure proper scale and proportions. They provide precise measurements of walls, rooms, and other features, allowing users to understand the actual size and layout of the space.
Proper scale ensures that the drawing accurately represents the real-world dimensions of the building or room. This is essential for planning furniture placement, determining traffic flow, and ensuring that all elements fit harmoniously within the space. Accurate proportions, on the other hand, maintain the correct relationship between different parts of the drawing, ensuring that the overall layout is balanced and visually pleasing.
Achieving accurate dimensions requires careful measurements and attention to detail. Architects and designers use measuring tapes, laser measuring devices, and other tools to capture precise dimensions of the space. They then transfer these measurements to the drawing, ensuring that the scale and proportions are maintained throughout the design process.
Accurate dimensions also facilitate communication between different stakeholders involved in the design and construction process. Contractors, builders, and interior designers rely on these drawings to execute the project according to the architect’s vision. Precise measurements help avoid costly errors and ensure that the final built space the intended design.
Overall, accurate dimensions are the foundation of effective example floor plan drawings. They provide a reliable representation of the space, enabling users to make informed decisions and ensuring a successful building or renovation project.
Detailed fixtures: Shows placement of doors, windows, and other elements.
Detailed fixtures in example floor plan drawings refer to the precise placement of doors, windows, and other essential elements within a building or room. These fixtures play a crucial role in defining the functionality, accessibility, and overall design of the space.
- Doors:
Doors are essential for connecting different rooms and providing access to the building. Example floor plan drawings indicate the location, size, and swing direction of each door. This information is crucial for ensuring proper circulation, accessibility, and adherence to building codes.
- Windows:
Windows provide natural light and ventilation to a space. Example floor plan drawings show the location, size, and type of windows used. This information helps determine the amount of natural light entering the room and the potential for cross-ventilation, affecting the overall comfort and energy efficiency of the building.
- Closets and storage:
Closets and storage areas are essential for organization and space management. Example floor plan drawings indicate the location, size, and type of closets and storage solutions used. This information helps users visualize the available storage space and plan for their belongings.
- Built-in features:
Built-in features, such as bookshelves, benches, and fireplaces, can enhance the functionality and aesthetic appeal of a space. Example floor plan drawings show the location and dimensions of these features, allowing users to understand their impact on the overall layout and design.
Detailed fixtures in example floor plan drawings provide valuable information for planning furniture placement, determining traffic flow, and ensuring the efficient use of space. They also assist in visualizing the overall aesthetic and functionality of the building or room, facilitating informed decision-making throughout the design and construction process.
Wall specifications: Indicates wall types, materials, and thickness.
Wall specifications in example floor plan drawings provide detailed information about the types of walls used in a building or room, their materials, and their thickness. Understanding these specifications is crucial for several reasons:
- Structural integrity:
Wall specifications indicate the type of wall construction used, such as load-bearing walls or non-load-bearing walls. Load-bearing walls support the weight of the building, while non-load-bearing walls divide interior spaces. This information is essential for ensuring the structural integrity and safety of the building.
- Material selection:
Wall specifications specify the materials used in the construction of the walls, such as drywall, concrete, or brick. Different materials have different properties, such as soundproofing, fire resistance, and durability. This information helps architects and designers select the most appropriate materials for the specific requirements of the space.
- Space planning:
Wall thickness affects the overall dimensions and layout of a room. Example floor plan drawings indicate the thickness of interior and exterior walls, allowing users to plan furniture placement, circulation paths, and the overall spatial relationships within the building or room.
- Compliance with codes:
Wall specifications must adhere to building codes and regulations, which set minimum standards for wall construction, materials, and thickness. Example floor plan drawings demonstrate compliance with these codes, ensuring the safety and habitability of the building.
Overall, wall specifications in example floor plan drawings provide critical information for understanding the structural integrity, material selection, space planning, and code compliance of a building or room. These specifications are essential for ensuring the safety, functionality, and aesthetic appeal of the built environment.
Room labels: Identifies the function of each room.
Room labels in example floor plan drawings are essential for identifying the intended function of each room within a building or structure. These labels provide a clear understanding of the spatial organization and flow of the building, facilitating efficient navigation and space planning.
- Clarity and organization:
Room labels help organize and clarify the floor plan drawing, making it easier to understand the layout and purpose of each room. They provide a quick visual reference for users, allowing them to quickly identify the location and function of different spaces within the building.
- Functional planning:
Room labels assist in functional planning by indicating the intended use of each space. This information is crucial for architects, designers, and occupants to plan furniture placement, circulation paths, and the overall functionality of the building. Clear room labels ensure that each space is designed and utilized in a manner that aligns with its intended purpose.
- Code compliance:
Room labels may also be required for compliance with building codes and regulations. These codes often specify the minimum room sizes and functions for different types of buildings, such as residential, commercial, and industrial. Room labels help demonstrate compliance with these regulations, ensuring the safety and habitability of the building.
- Communication and collaboration:
Example floor plan drawings with clear room labels facilitate effective communication and collaboration among architects, designers, contractors, and other stakeholders involved in the design and construction process. Standardized room labels ensure a common understanding of the building’s layout, reducing the potential for misinterpretation and errors.
Overall, room labels in example floor plan drawings play a vital role in conveying the function and organization of a building or structure. They enhance clarity, support functional planning, ensure code compliance, and facilitate effective communication during the design and construction process.
Furniture layout: Illustrates potential furniture arrangements.
Furniture layout in example floor plan drawings provides a visual representation of how furniture can be arranged within a room or space. It illustrates the potential placement of sofas, chairs, tables, and other furniture pieces, helping users visualize the functionality and flow of the space.
- Space planning:
Furniture layout assists in space planning by allowing users to experiment with different furniture arrangements and configurations. It helps determine the optimal placement of furniture to maximize space utilization, ensure comfortable circulation paths, and create a cohesive and aesthetically pleasing environment.
- Functionality:
Furniture layout considers the functional requirements of the space. It takes into account the intended use of each room and the activities that will take place within it. By carefully planning the furniture layout, users can create spaces that are both functional and inviting, meeting the specific needs of the occupants.
- Visual appeal:
Furniture layout contributes to the overall visual appeal of a space. It allows users to experiment with different styles, colors, and textures to create a harmonious and visually pleasing environment. By carefully selecting and arranging furniture pieces, users can enhance the aesthetics of the space and create a desired ambiance.
- Communication and collaboration:
Furniture layout drawings facilitate communication and collaboration among architects, designers, and clients. They provide a shared visual representation of the proposed furniture arrangements, enabling stakeholders to discuss and refine the design. Clear and well-defined furniture layouts reduce the potential for misinterpretation and ensure that the final design meets the expectations of all parties involved.
Overall, furniture layout in example floor plan drawings plays a crucial role in space planning, functionality, visual appeal, and communication during the design process. It helps users visualize the potential furniture arrangements, optimize space utilization, and create functional and aesthetically pleasing environments.
Circulation paths: Highlights traffic flow and accessibility.
Circulation paths in example floor plan drawings represent the designated routes for movement within a building or space. They indicate the flow of traffic, ensuring that occupants can move safely and efficiently from one area to another. Circulation paths consider various factors, including:
- Accessibility: Circulation paths must be accessible to all users, including individuals with disabilities. This means providing ramps, elevators, and other accommodations to ensure that everyone can navigate the space.
- Safety: Circulation paths should be designed to minimize safety hazards. This includes providing clear sight lines, avoiding narrow or congested areas, and separating pedestrian and vehicular traffic.
- Efficiency: Circulation paths should be designed to facilitate efficient movement. This means minimizing the distance between frequently used spaces and avoiding unnecessary detours.
To represent circulation paths in example floor plan drawings, architects and designers use a variety of symbols and conventions. Common symbols include arrows to indicate the direction of traffic flow, dashed lines to represent potential paths, and shaded areas to indicate primary circulation routes. By clearly defining circulation paths, floor plan drawings help ensure that the building or space is easy to navigate and accessible to all users.
Circulation paths also play a crucial role in space planning and layout. They influence the placement of furniture, equipment, and other elements within a room or building. By considering circulation paths early in the design process, architects and designers can create spaces that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
Overall, circulation paths in example floor plan drawings are essential for ensuring the safety, accessibility, and efficiency of a building or space. They provide a visual representation of traffic flow, guiding occupants through the space and facilitating seamless movement.
Well-planned circulation paths contribute to the overall success of a design by enhancing the user experience, improving functionality, and creating a sense of flow and harmony within the built environment.
Lighting plan: Indicates lighting fixtures and their placement.
A lighting plan in an example floor plan drawing provides a detailed representation of the lighting fixtures and their placement within a building or space. It indicates the type, quantity, and location of light sources, ensuring adequate illumination and creating the desired ambiance in each area.
Lighting plans consider various factors, including the function of the space, the amount of natural light available, and the desired aesthetic effect. Architects and designers use a variety of symbols and conventions to represent lighting fixtures in floor plan drawings. These symbols indicate the type of fixture, such as recessed lighting, pendant lights, or wall sconces, as well as their location and orientation.
Proper lighting is crucial for creating a comfortable and functional environment. A well-lit space enhances visibility, reduces eye strain, and contributes to the overall well-being of occupants. Lighting plans help ensure that each area within a building or space receives the appropriate amount of illumination for its intended use. This includes providing adequate task lighting for workspaces, ambient lighting for general illumination, and accent lighting to highlight specific features or create a desired ambiance.
Lighting plans also play a role in energy efficiency. By carefully selecting and placing lighting fixtures, architects and designers can minimize energy consumption while maintaining adequate illumination. This involves considering the use of energy-efficient lighting technologies, such as LED lights, and incorporating natural light whenever possible to reduce reliance on artificial lighting.
Overall, lighting plans in example floor plan drawings are essential for ensuring the functionality, comfort, and energy efficiency of a building or space. They provide a visual representation of the lighting fixtures and their placement, guiding the selection and installation of lighting systems that meet the specific requirements of each area.
Compliance with codes: Adheres to building regulations and standards.
Compliance with codes in example floor plan drawings ensures that the design and construction of a building or space adheres to established building regulations and standards. These codes are set by local authorities and governing bodies to ensure the safety, accessibility, and structural integrity of buildings. By complying with these codes, architects and designers can create spaces that meet minimum requirements and provide a safe and habitable environment for occupants.
- Building codes:
Building codes regulate various aspects of building design and construction, including structural requirements, fire safety, accessibility, and energy efficiency. Example floor plan drawings must demonstrate compliance with these codes to obtain building permits and ensure the safety and habitability of the structure.
- Fire safety codes:
Fire safety codes specify requirements for fire-resistant materials, fire detection and suppression systems, and emergency egress. Example floor plan drawings must show the location of fire exits, fire-rated walls, and other fire safety features to ensure that the building meets fire safety regulations.
- Accessibility codes:
Accessibility codes ensure that buildings are accessible to individuals with disabilities. Example floor plan drawings must indicate the provision of ramps, elevators, accessible restrooms, and other features to comply with these codes and provide equal access to all occupants.
- Energy efficiency codes:
Energy efficiency codes set standards for the energy performance of buildings. Example floor plan drawings must demonstrate the use of energy-efficient building materials, appliances, and systems to comply with these codes and reduce the environmental impact of the building.
Overall, compliance with codes in example floor plan drawings is essential for ensuring the safety, accessibility, and sustainability of buildings. By adhering to these codes, architects and designers can create spaces that meet the minimum requirements set by regulatory bodies and provide a safe and habitable environment for occupants.










Related Posts